And you don’t have to take my word for it. Whole books have been written on the subject!
But in case you don’t want to read three books—or even one—here are some highlights.
Undergarments
Bras
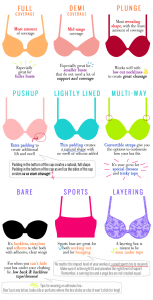
Underwire bras can kill you by acting as conductor if you are struck by lightning. Not likely, but possible. On the other hand, underwires digging into your body is common, and can be painful, cause skin irritation, even bruising.
Regularly wearing a push-up or padded bras, on the other hand, constantly pull the breast against gravity and put pressure on the delicate tissues of the lower breast. If these tissues separate from the main body tissues, it causes sagging.

Ill-fitting bras, especially for the well-endowed, can lead to pain in the neck, shoulders, back, and chest. Research by Rouillon on women 18-35 showed that women who did not wear bras developed more muscle tissue to provide natural support. Hmm… One study in 1991 suggested that premenopausal women who went bra-less had half the risk of breast cancer.
Thongs/ G-Strings


Thong panties increases the likelihood of getting urinary tract infections. Thongs that have a tendency to slide forward transfer bacteria to the genitals. And these panties have been linked to the development of hemorrhoids. (To avoid embarrassing confusion, remember that “thongs” in Australia are flip-flop shoes. Scanty panties are called “G-strings.”)
Boxers or Briefs?

In 2018, NPR reported on research that showed that men who wear tight-fitting briefs had sperm counts 17% lower than boxer wearers. This is probably an effect of heat: men’s testicles hanging below the torso stay cooler by 4-6 degrees. By extension, should men who want to father children wear no pants at all? Kilts or kimonos?
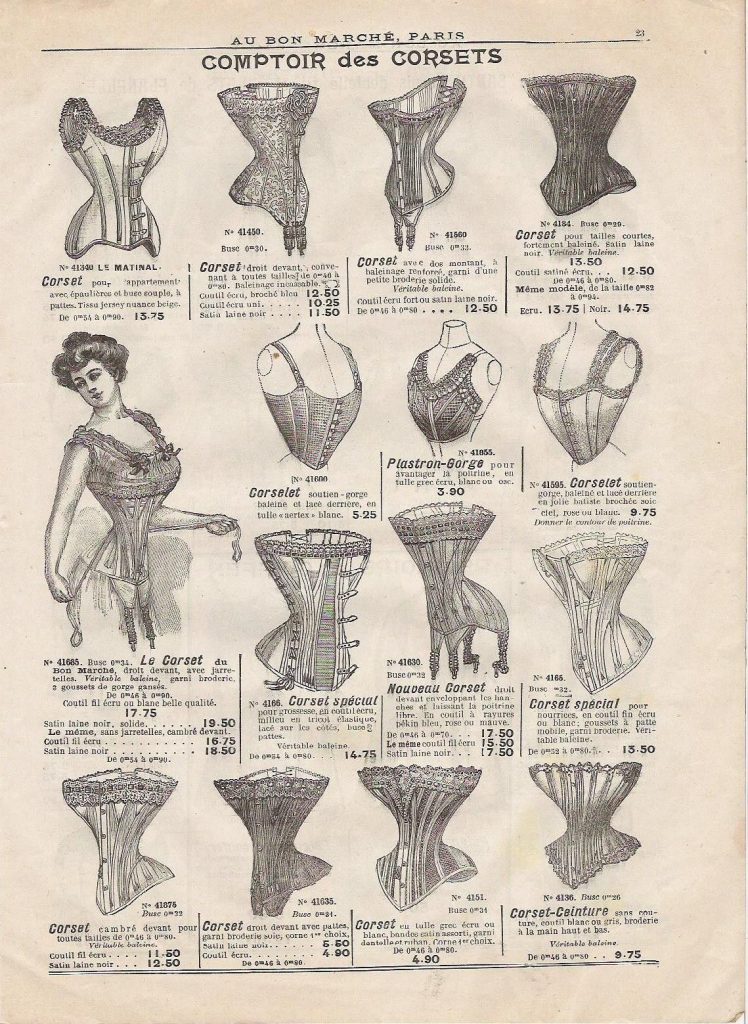
Corsets


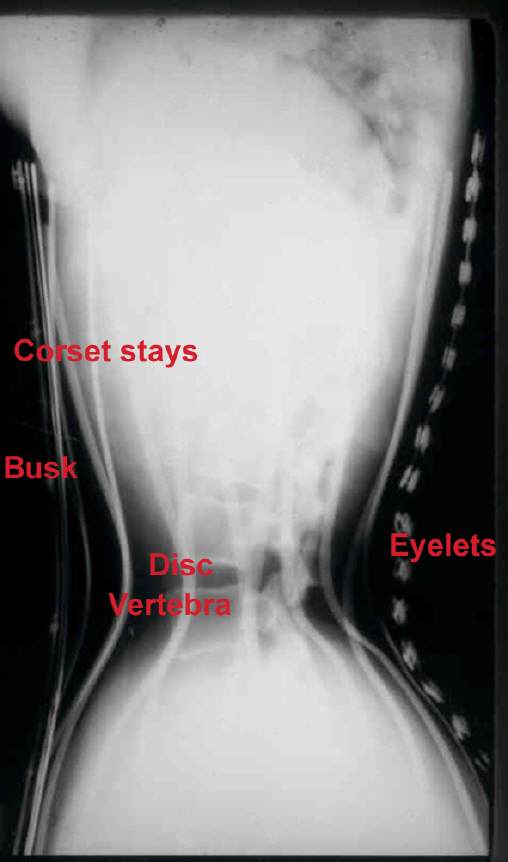
“Corset” probably brings to mind the lace-up garment of the 1890s, in ads that claimed they could reduce a 27-inch waist to 18 inches. The resulting displacement of internal organs caused constipation and weakened a woman’s back muscles, sometimes to the point of being unable to remain upright without the support of the corset.
This style of corsets today are mostly relegated to dress-up, sex play, or limited to occasional use.

A modern version would be shape wear. When worn daily, it puts unwanted and unnecessary pressure on internal organs, resulting in acid reflux because of pressure on the stomach, and possible nerve damage by constricting your sides and thighs.

As an interesting historical side note, both lace-up and compression corsets have been marketed to men as well as women.
Petticoats and Slips

In addition to trying to shrink their waists, American and European women wore big cage-like devices under their skirts to make their waists look even smaller. The hoop skirt (aka, a cage crinoline) was made of a fabric petticoat with channels to hold thin strips of wood, whalebone, or other stiffenings, and a tie to secure it at the waist.

The bigger the hoop, the more it inhibited women’s mobility. In addition, they were very flammable, making them particularly dangerous around candles, lanterns, fireplaces, and all those other commonly burning things found in the average 19th Century household. In England in the 1860s, as many as 300 women a year died this way.

Bathing Suits


By exposing large amounts of skin to sunlight, a bathing suit can contribute to some types of skin cancers.
For women, the lack of support in bathing suit tops can contribute to the same problems as ill-fitting bras.

Sitting around in a wet bathing suit for hours on end may lead to a yeast infection or UTI, plus anything associated with bacteria in the water.
Advice: change out of wet suits ASAP and use plenty of sunscreen. Swimsuits with long sleeves or pants provide better sun protection but increase the risk of fabric filled with bacteria.
Yoga Pants
For all that they are comfortable and versatile, yoga pants are susceptible to all the problems listed for compression clothing. You might get chaffing from running, inflamed hair follicles (from bacteria) or ingrown hairs (from compression), as well as fungal infections.
Shoes
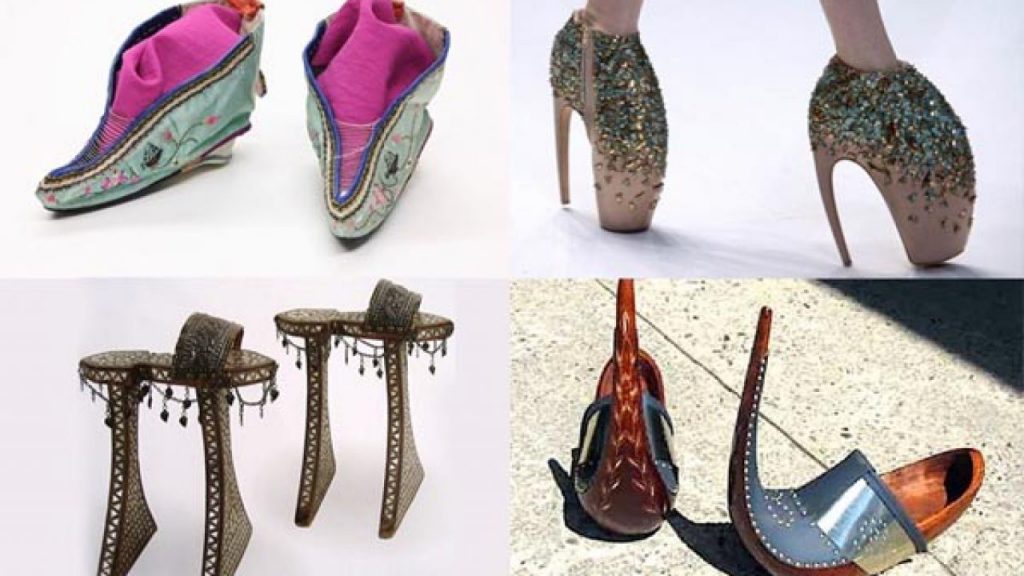

High Shoes

High heels misalign one’s posture, often leading to long-term damage to knees, spine, hips, and leg muscles. They also increase the risk of tripping, falling, and rolling one’s ankles, sometimes with fatal results. Wearing designer shoes (e.g., Jimmy Choo, Manolo Blahnik, or Christian Lououtin) that cost a fortune still inhibit a woman’s mobility.

In 16th century Italy, aristocratic women wore tall platforms called chopines, made of wood, covered in leather, and decorated. The women were essentially walking on short, fat, stilts and unable to move freely. But then, there were few occasions for them to go out, unless it was to display the wealth of the family.


Similar footwear has been worn for practical or ornamental purposes in many areas. Variations of Japanese geta kept fancy aristocrats and peasant farmers out of mud and snow. Sudanese Nuba wooden sandals, Dutch klompen, Korean namakshin, Cantabrian Spanish albarcas, and British pattens were all variations of risers worn over or clipped to the shoe.

Platform shoes are still with us.
Low Shoes

Flip-flops have been linked to foot, ankle, and knee pain. In addition, the exposed foot is vulnerable to falling objects, getting stepped on or rolled over, an well as tripping or hitting one’s toes into whatever is around.

Crocs, rubber slip-on shoes, are very popular at the moment but with their own dangers. According to the Consumer Product Safety Commission, nearly 200 wearers (mostly kids) have been injured when their Crocs were snagged between the moving treads of an escalator.

Flat shoes that don’t offer proper support can cause abnormalities in how one walks and runs.
Small Shoes
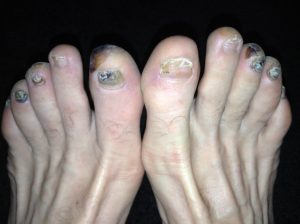
Shoes that are too small in any way are likely to cause discomfort, even if only worn briefly. Wearing shoes that are too small for extended periods of time can cause serious damage to feet. Marathon runners are advised to buy shoes one to one-and-a-half sizes larger than normal to account for swelling caused by hours of pounding the pavement. Not doing so is likely to cause ingrown toenails, lost toenails, cysts on top of the foot, and nerve damage in the toes and arches.
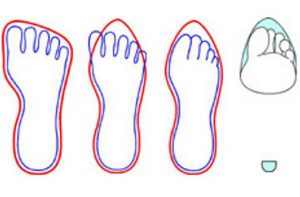
Pointy-toe shoes harm feet by squeezing and molding the foot into an unnatural shape. They distort individual toes, and swelling between toes three and four can pinch a nerve most painfully.


Dancers frequently suffer foot problems caused by shoes. Some dancers deliberately wear shoes slightly too small to allow for better grip with the floor or so the material conforms better to the shape of the foot. Tabi (somewhere between shoes and socks) worn by traditional Japanese dancers and ghillies (soft shoes) worn by Irish dancers are often worn a half size too small. Ballet pointe shoes, no matter how well fitted, force the foot into a cramped position while dancers balance their entire weight on their toes.

The Chinese practice of foot-binding is the most extreme example of shoes mangling women’s feet. Lotus feet were highly valued. For one thing it denoted wealth: the woman didn’t have to work in the fields and/or being carried everywhere implied she would always be rich enough for such service. Walking at all involved a sway of the hips that was thought to be sexy.

Foot binding began in infancy or toddlerhood. It was painful at best, and if the feet became infected, could cause septic shock. The last factory producing lotus shoes didn’t close until 1999.
Accessories
Jewelry
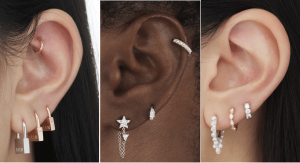
Big, heavy earrings may lead to inadvertently stretching or tearing one’s earlobes. They can get hooked onto objects or clothing, and even tear the earlobe.
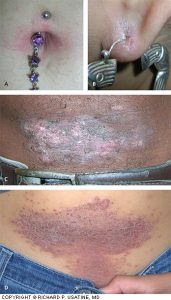
Chunky, heavy necklaces and chains put pressure on your neck, back, and chest.
Oversized bracelets can cause wrist, arm, hand, and finger pain.
Avoid nickel, found in many pieces of clothing and accessories: it is the cause of one of the most common allergic reactions. Stick with stainless steel, silver, gold, or platinum, depending on your taste and budget.
Hats

Wearing a hat per se probably doesn’t cause hair loss, but any tight headgear could break hair follicles, creating bald patches known as friction alopecia. Wearing a hat while sweating can irritate your scalp.

In 1600s France, aristocratic women wore a “pouf,” something between a hat and a hairstyle. Elaborate piles of flowers, feather, ribbons, gauze, or whatever. At least one woman died when her enormously tall pouf hit a candle in a chandelier and caught fire.

Not exactly a hat, but a headpiece nonetheless, in the 1800s men shaved their heads and wore perukes. The lice lived in the wig rather than on the body, and the wig could be sent to the wigmaker to be boiled and deloused.
Neckware

Wearing scares may lead to strangulation, either intentional or accidental. (Think Isadora Duncan.) Thirty-five people a year are choked to death by their own scarves.

Around the turn of the 20th century, men wore stiffly starched collars that were nicknamed “father killers.” They were so high and stiffly starched that if a man passed out wearing one, it would cut of his air supply.

Neckties are to men what scarves are to women, only less so: ten deaths per year are attributable to neckties.
Bags

Heavy shoulder bags, handbags, and purses are typically carried on the same shoulder or arm, causing neck, shoulder, and back pain as well as throwing the body out of balance, forcing the other side to compensate, leading to all-over discomfort.

Heavy backpacks without a waist strap and book bags can also cause neck, shoulder, and back strain, as well as long-term damage to one’s posture. Advice: lighten the load!
General Hazards in Clothing

Skin-tight clothing —everything from skinny jeans to shape wear and compression clothing—has been linked to all sorts of health problems: heartburn/acid reflux, testicular damage, and compartment syndrome (in which pressure builds up in constricted muscles, potentially life-threatening), and nerve damage. Such clothes can cause tingling in and numbness in feet and legs.

Any clothing that is excessively large presents a danger. A train on a skirt can be caught under bystanders’ feet, wrapped around wheels, or snagged by anything on the ground. Trailing sleeves have a tendency to knock things over or catch any open flames. Extra padding anywhere can put uneven weight on the body or cause the wearer to bump into things. Trouser legs or skirts that are too long are a tripping hazard. Tails always seem to have a tendency to be caught in doors.

Fabrics (including shoes) that don’t breathe often cause general discomfort, as well as dermatitis and fungal overgrowth (e.g., athlete’s foot). Stiff fabrics or scratchy ornamentation can cause chafing and abrasions.
Chemicals in Clothing

Skin is the largest organ of the body, and it’s capable of absorbing substances—not only from skincare products and makeup, but also from clothing. Chemicals absorbed through the skin go into the blood stream, which has access to all the internal organs.

Warning: the following story is disgusting on many levels. A woman bought a black dress at an upscale shop in Fredericksburg, but returned it a few days later. Another woman bought the dress, and developed such serious health problems that she nearly died. It turns out that the first woman’s mother had died and the black dress was put on her for her viewing. It was thoroughly contaminated with formaldehyde. Formaldehyde and p-Phenylenediamide (in black clothing and leather dies) are in the products of 14 big-brand clothing manufacturers.

Formaldehyde—used to prevent mildew growth and inhibit wrinkling—is particularly harmful, and the U.S. does not restrict its use. (Sri Lanka and China two of the worst offenders, and major sources of inexpensive clothing.) Formaldehyde has been linked to an increase in lung cancer, difficulty breathing, and itchy eyes/nose/throat.

Side effects run from mild dermatitis to disruption of the endocrine system to cancer. However, different chemicals can affect different organs.

The U.S. doesn’t require disclosure of any of the chemicals used during production even though, according to Emma Loewe of MindBodyGreen, (How Worried Should You Be About Chemicals in Your Clothes), “…by some estimates there are upward of 250 ‘restricted substances’ used in textile manufacturing that pose potential health concerns.’”
Avoid Being Poisoned by Your Clothes

- Because synthetics carry a heavier load of harmful chemicals, necessary to produce them, choose organic, natural fibers such as cotton, linen, jute, silk, and hemp.
- Also avoid clothing labeled flame retardant or as wrinkle, stain, odor, or water resistant because these effects are achieved through chemical additives.
- If you need synthetics, choose brands that use “rPet” or recycled polyester (e.g., Adidas and Athleta do this).
- Choose clothes colored with natural dyes. If you don’t know, go for lighter colors, which contain less dye.
- Wash before wearing to remove any surface chemicals picked up during packaging and shipping.
- If you notice any kind of reaction to your clothing, discontinue wearing and consult a medical professional as warranted.
- And last but not least: don’t wear anything that makes you feel self-conscious or nervous just because it is “in.”

Writers Note: Surely at least some of your characters make hazardous clothing choices!
- A cunning murderer who makes it look like an accidental suffocation or poisoning
- An advocate on behalf of someone who has suffered long-term effects of harmful dyes or chemicals
- A character knowingly wearing harmful clothing in an effort to look fashionable
- A character who refuses to wear harmful clothing and is shunned
- A lower-class or impoverished character without the money to wear organically made or custom fitted clothing