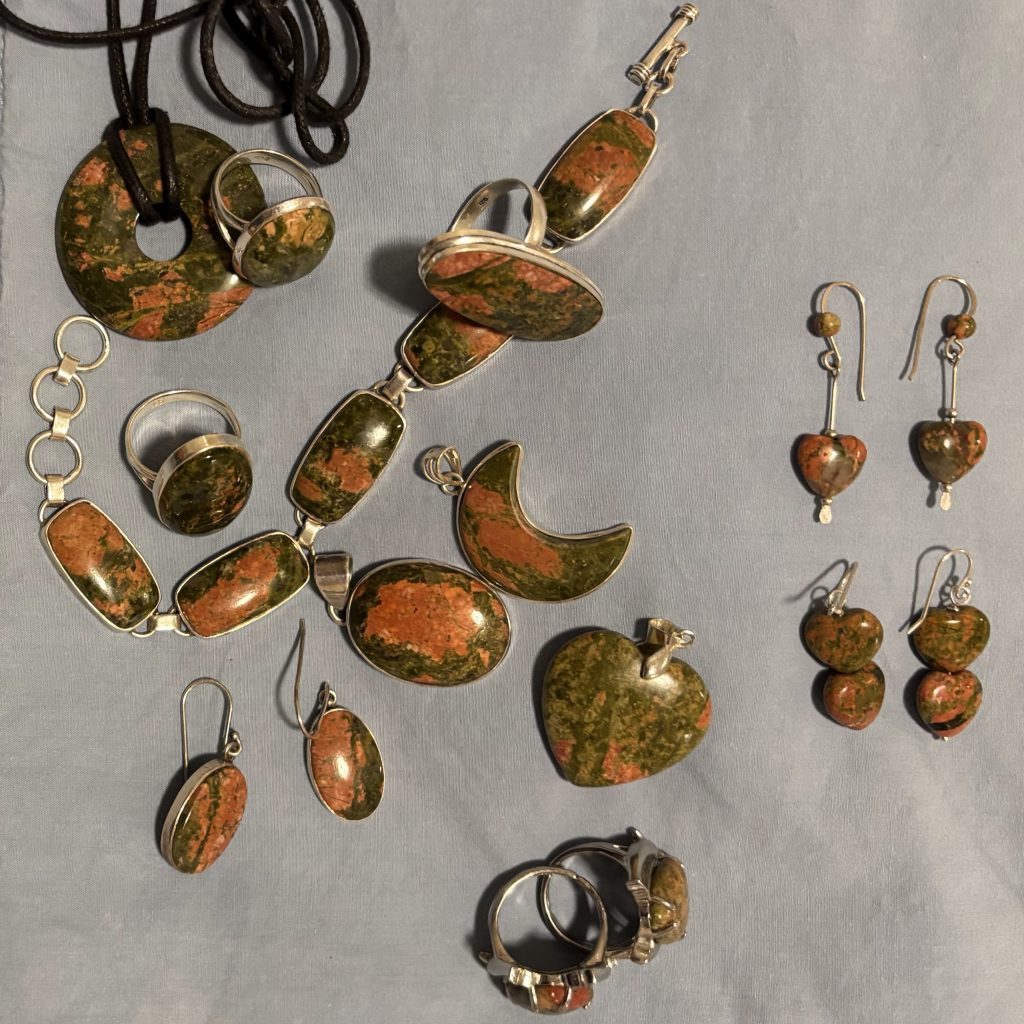I’m a jewelry junkie. Some years ago, at a shop in the Blue Ridge, I bought several pieces of a lovely sage green and salmon colored stone. The clerk identified it as unakite, and said it is the state gem for Virginia—which pleased me a great deal. Apparently, it is abundant in the Blue Ridge.
Alas, when I started looking for official Virginia symbols, unakite is NOT among them. Virginia Opal is an unofficial State Gem. The official Virginia Rock or Stone is Nelsonite (2016), not nearly as attractive (IMHO).
Earliest Virginia Symbols
Virginia has a rich collection of official state symbols that reflect its history, culture, and natural heritage.
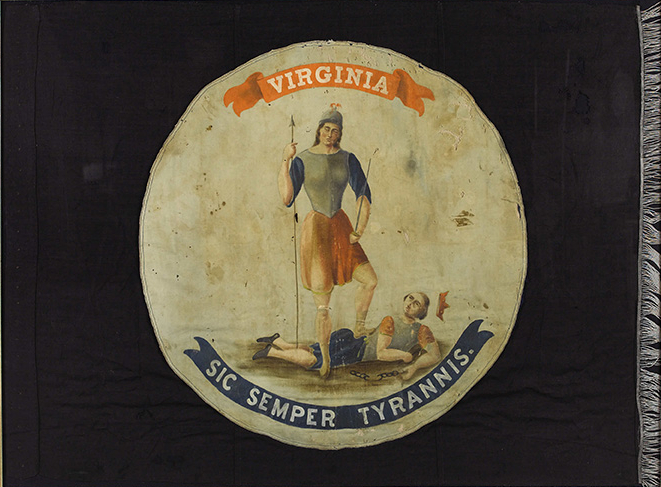
Most of Virginia’s official symbols were designated in the late 20th century, with the significant exceptions of the state motto and seal. Virginia officially declared its Great Seal—designed by George Wythe—on July 5, 1776 (standardized in 1950). It is one of Virginia’s earliest and most significant symbols, adopted during the American Revolution. The State Motto was proposed by George Mason to be included in the State Seal in 1776. Translated from Latin as “Thus Always to Tyrants”, it means that tyrants will eventually be overthrown.
The Virginia state flag prominently features the seal. Although the seal appeared on military flags before April 30, 1861, that is the year that the state legislature placed it on a blue field as the official state flag during the Civil War era (see the banner picture for this blog entry). The flag was last updated in 1950.
Virginia Animal Symbols
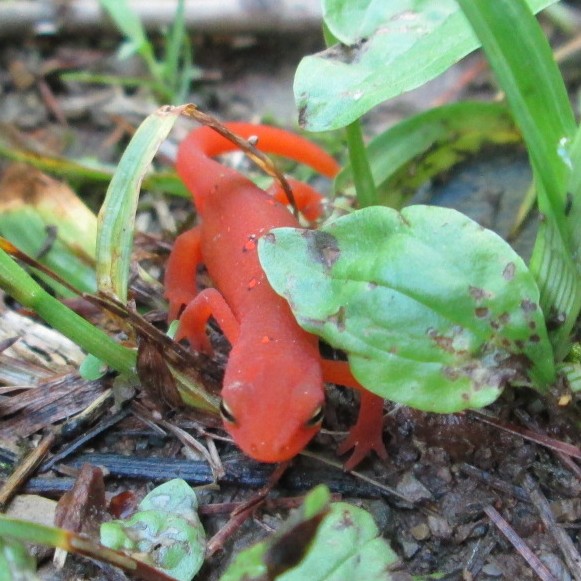
State Amphibian: Red Salamander (2018). This amphibian, unique among its kind, can breathe through its skin.
State Bat: Yes, we have one! It’s the Virginia Big-Eared Bat (Corynorthinos townsendii virginianus). In 2005, legislators chose the bat for its name and endangered status. At the time, Gov. Mark Warner said that a state bat “is no more absurd than the state beverage.” (See below.)
State Bird: Northern Cardinal. Actually, the cardinal is the most popular state bird, also symbolizing Kentucky (1926), West Virginia (1927), Illinois (1929), Indiana (1933), Ohio (1933), North Carolina (1943), and—bringing up the rear—Virginia (1950). If you cross-reference, you will note that five of these states were, originally, part of Virginia! (See below.)
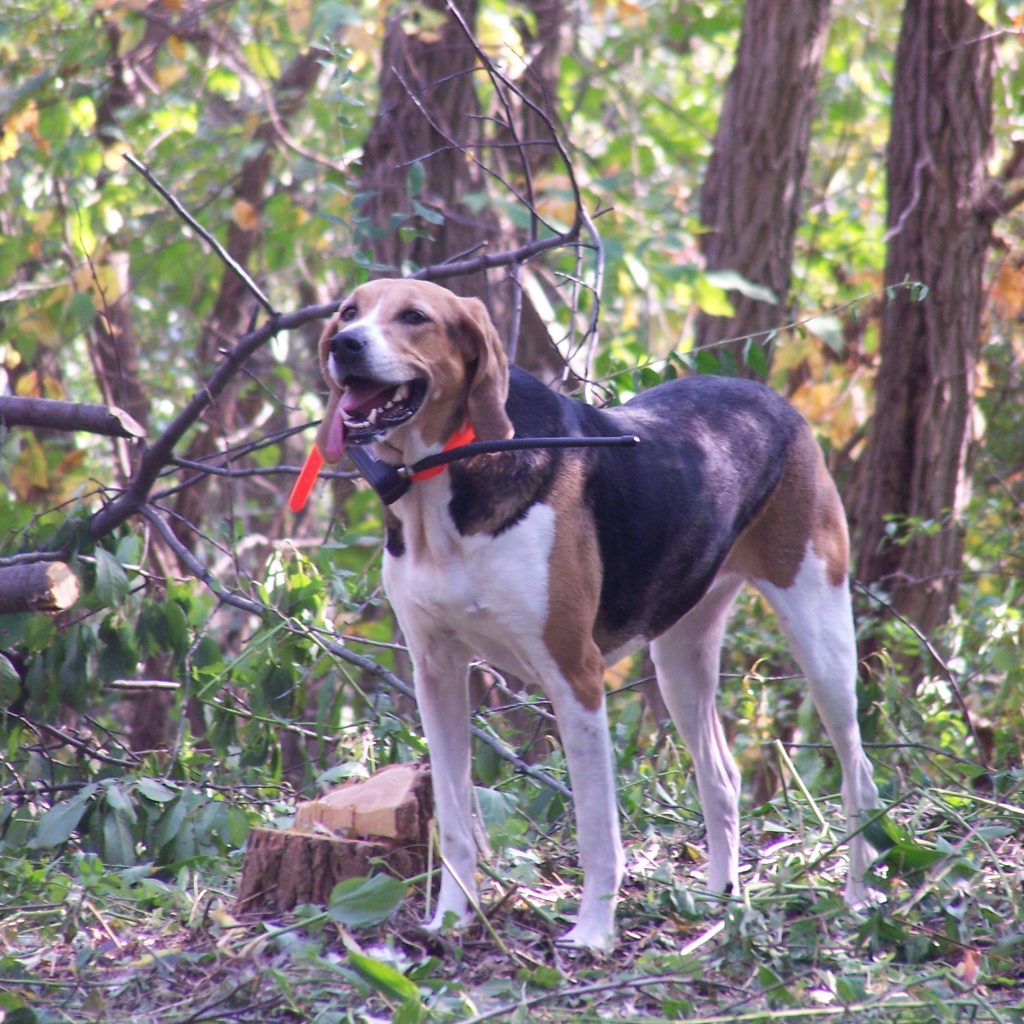
State Dog: American Foxhound (1966). Fox hunting started in Virginia around 1700 as a popular sport among the gentry, and was a traditional activity ever since.
State Freshwater Fish: Brook Trout (1993). Brook trout are actually not technically a “trout”. They are in the Char family, although they are the most “Trout Like” in their family.
State Saltwater Fish: Striped Bass (2011). This fish has distinctive horizontal stripes running along silvery bodies—which help camouflage the fish by breaking up its outline in the water, making it harder for predators to spot.
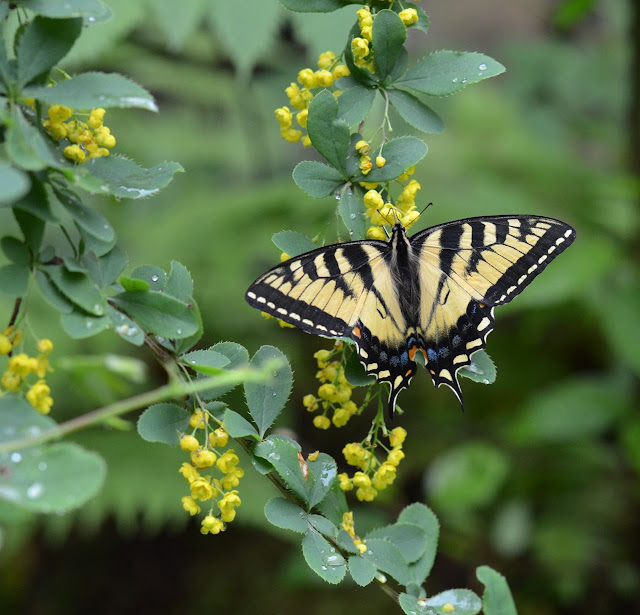
State Insect: Tiger Swallowtail Butterfly (1991) The Eastern Tiger Swallowtail butterfly (Papilio glaucus) is a common but beautiful butterfly that regularly comes to my yard, especially to my butterfly bush for nectar. Keen observers can find them anywhere east of the Mississippi river and a bit farther west into the Great Plains states. There are also populations in several Mexican states.
State Pollinator: European Honeybee (2024) These bees use a “waggle dance” to communicate the location of food sources to other foragers, indicating both direction and distance. So, when you see one, you are likely to see many. They seem to especially enjoy my hyssop, a perennial plant that smells like licorice.
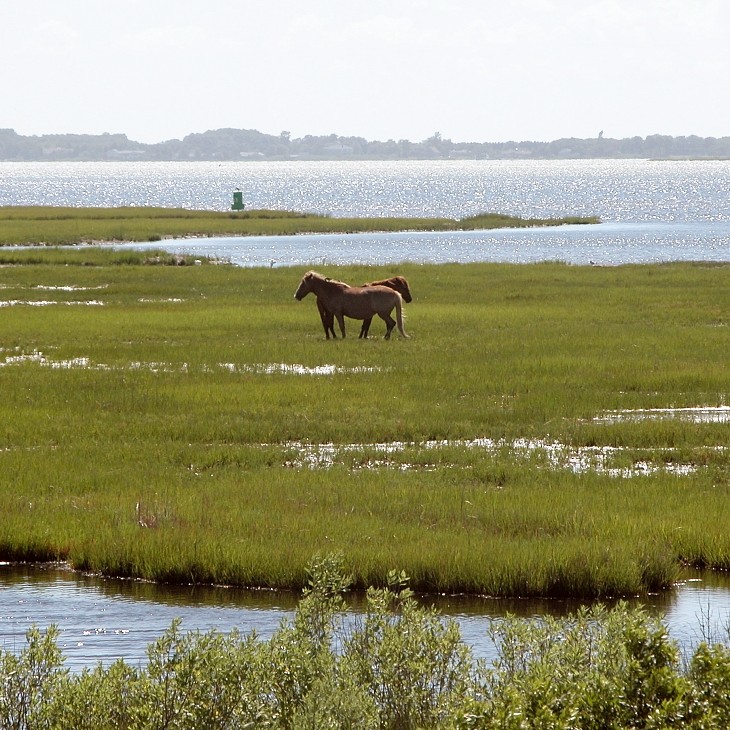
State Pony: Chincoteague Pony (2023). These ponies weren’t an official breed until 1985! Their historical home of Assateague Island straddles Maryland and Virginia. The Maryland herd is controlled with the use of contraceptive vaccines. The Virginia side uses an annual Pony Swim and auction to control the island population.
State Reptile: Eastern Garter Snake (2016) In 2016, Aiden Coleman, then 11 years old, successfully petitioned the Virginia Senate to name the Eastern Garter Snake (Thamnophis sirtalis sirtalis) an official symbol of Virginia. Though only mildly venomous, these snakes can emit a foul odor when threatened, which some have described as “something like a cross between a soiled diaper and a skunk.” Garter snakes, unlike most reptiles, give birth to live young rather than laying eggs.
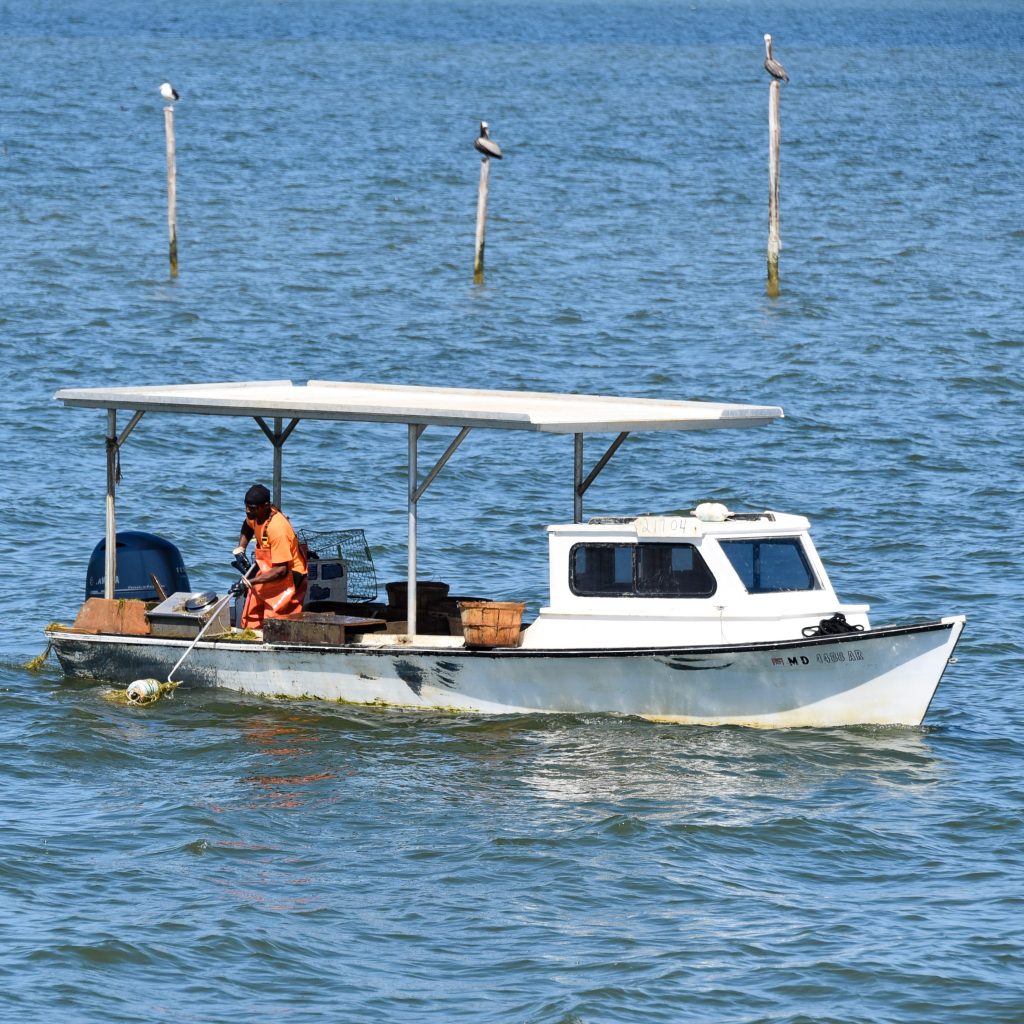
State Shell: Eastern Oyster (1974). The Eastern Oyster (Crassostrea virginica) is the only species of oyster native to this region. It is a valued food source for humans and other species. As filter feeders, they help clean the water. Centuries ago, in some places, oyster shell reefs were so big that ships had to navigate around them. Since then, in many areas, the populations have dwindled to just a few percent of what they once were due to disease, over-harvesting, habitat loss, and poor water quality.
Other Virginia Symbols
State Beverage: Milk (1982). Milk is the state drink of twenty U.S. states, from New York to North Dakota. This is largely due to lobbying efforts from the dairy industry in the 1980s.
State Boat: Chesapeake Bay deadrise (1988). Very few other states have a state boat, but a couple of exceptions are Maryland (skipjack) and North Carolina (shad boat).
State Dance: Square Dance (1991). Among the 29 states having official state dances, square dancing is the most popular—24!
NB: some states have more than one official dance.
State Flower: American Dogwood (Cornus florida), 1918. Thomas Jefferson grew American Dogwood on his Monticello estate in the 1770s. Legislators chose it as the official flower in 1918. In 1956, it also became the official State Tree.
State Fossil: Chesapecten jeffersonius (1993). This is a fossilized form of an extinct scallop, which lived between four and five million years ago on Virginia’s coastal plain. Colonists first described this distinct fossil in 1687.
State Slogan: VIRGINIA IS FOR LOVERS (1969). The slogan earned a mention in the Madison Avenue Advertising Walk of Fame in 2009, and Forbes declared this one of the top ten advertising campaigns of all time. When the Central Virginia Chapter of Sisters in Crime wanted to use “Virginia is for _“ in a book title, permission was denied for “Murders” but approved for “Mysteries.”
State Spirit: George Washington’s Rye Whiskey (2017) Mount Vernon staff reconstructed George Washington’s original recipe and distilled this whiskey using 18th century methods.
State Song: The state song has gone through some changes over the years. From 1940 to 1997, the official state song was “Carry Me Back to Old Virginny” by James A. Bland. Today, there are two! In 2015, the legislature officially recognized “Our Great Virginia” (traditional), and “Sweet Virginia Breeze” (popular).
Honorable Mentions
In addition to unakite, Virginia has several distinct resources that many people assume must be official symbols.
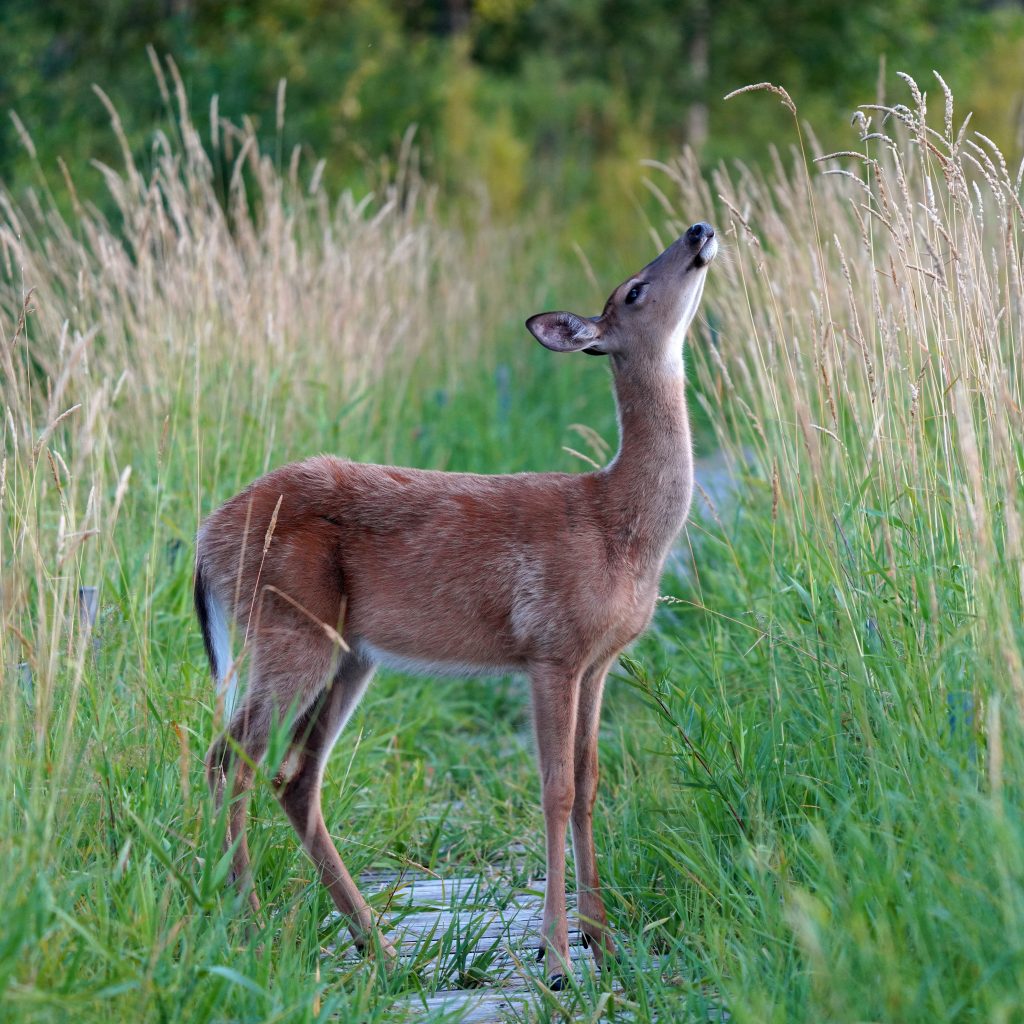
State Animal: Virginia Deer (White-tailed Deer). As far as I could determine, despite showing up on various lists, the white-tailed deer has not been officially designated as the state animal of Virginia. However, its scientific name, Odocoileus virginianus, reflects its historical significance and abundance in the state. Ever popular, it’s the official animal of 10 states other than Virginia.
State Fruit: Tomato. Although one list of state symbols included this, as far as I can find, Virginia does not have an official state fruit, tomato or otherwise. It’s just as well! Although botanically a fruit, the tomato is legally a vegetable for import/export purposes, and is certainly used as such!
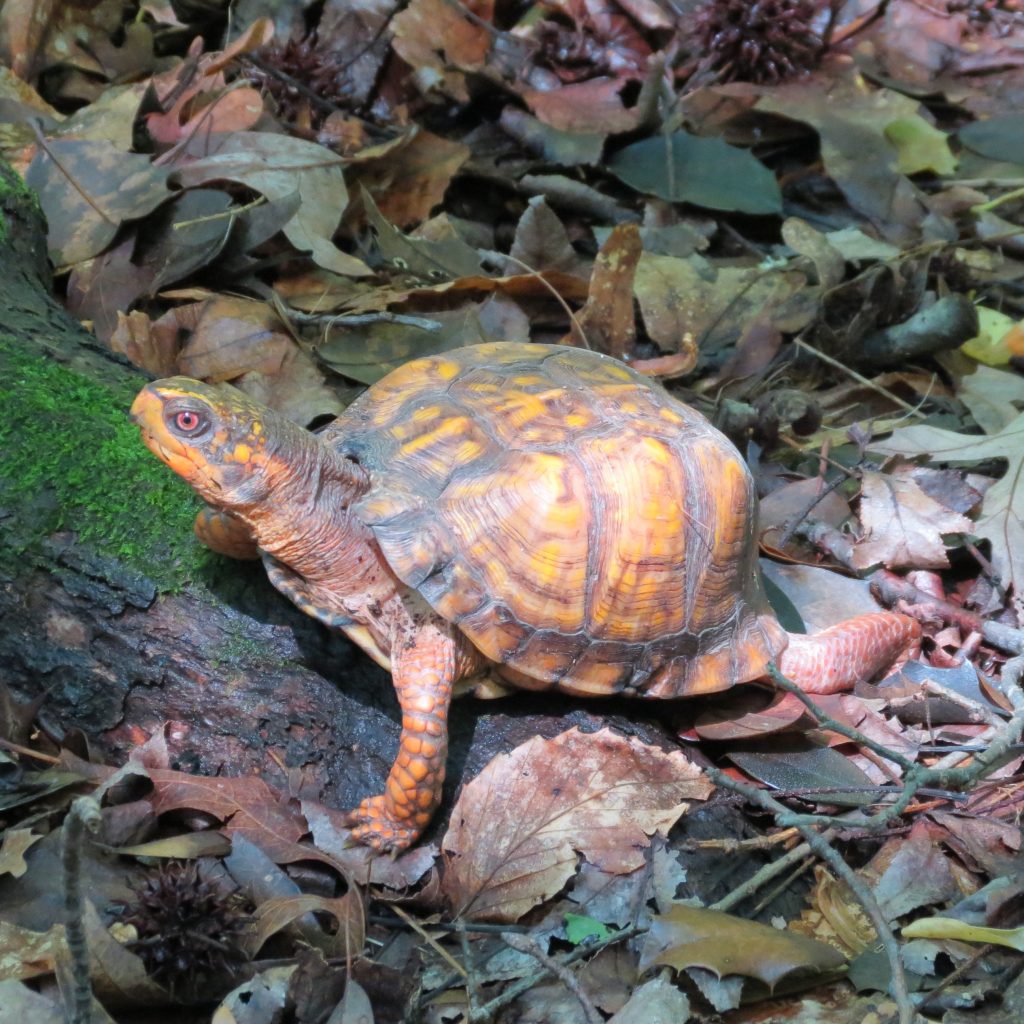
State Turtle: Lawmakers considered naming the Eastern Box Turtle (Terrapene carolina carolina) an official state symbol in 1999 and 2009, but they ultimately rejected it. I’m including it here because (in my opinion), it should be a Virginia symbol; it’s both adorable and interesting! I’ve loved these turtles since graduate school when I did research with them. They tend to be solitary, so a female can fertilize eggs up to 4 years after mating. Signs of sex include eye color, shell pattern, and shell shape. Females have red eyes, a simpler shell pattern, and straight-sided shells. Males have brown eyes and shells with a more vivid pattern, slightly flared at the bottom edge.
Unofficial Virginia Nicknames
Besides official symbols, several more designations for Virginia are traditionally acknowledged.
Mother of States: Since its settlement in 1606, Virginia has been carved into eight more states: Illinois, Indiana, Kentucky, Michigan, Minnesota, Ohio, West Virginia, and Wisconsin.
Mother of Presidents: George Washington, Thomas Jefferson, James Madison, James Monroe, William Henry Harrison, John Tyler, Zachary Taylor, and Woodrow Wilson all were born in Virginia.
NB: Seven U.S. presidents were born in Ohio, too: Ulysses Grant, Rutherford Hayes, James Garfield, Benjamin Harrison, William McKinley, William Howard Taft, and Warren G. Harding.
Old Dominion: A popular legend states that Charles II referred to Virginia as the Old Dominion. Virginia has a public university by that name.
And for a mostly unrelated fact and opinion, included because I was born and reared in Ohio and happen to know it: the official State Beverage for Ohio is tomato juice. The Ohio General Assembly made tomato juice Ohio’s official beverage in 1965. So far, it is the only state to appreciate tomatoes in that way. At that time, Ohio was a leading producer of tomatoes in the United States, second only to California. And in my opinion, Ohio tomatoes have it all over Hanover tomatoes, much lauded here in Virginia.
Bottom Line: Official state symbols celebrate natural beauty, wildlife, and cultural heritage, a mosaic of identity for a state, and Virginia is no exception.