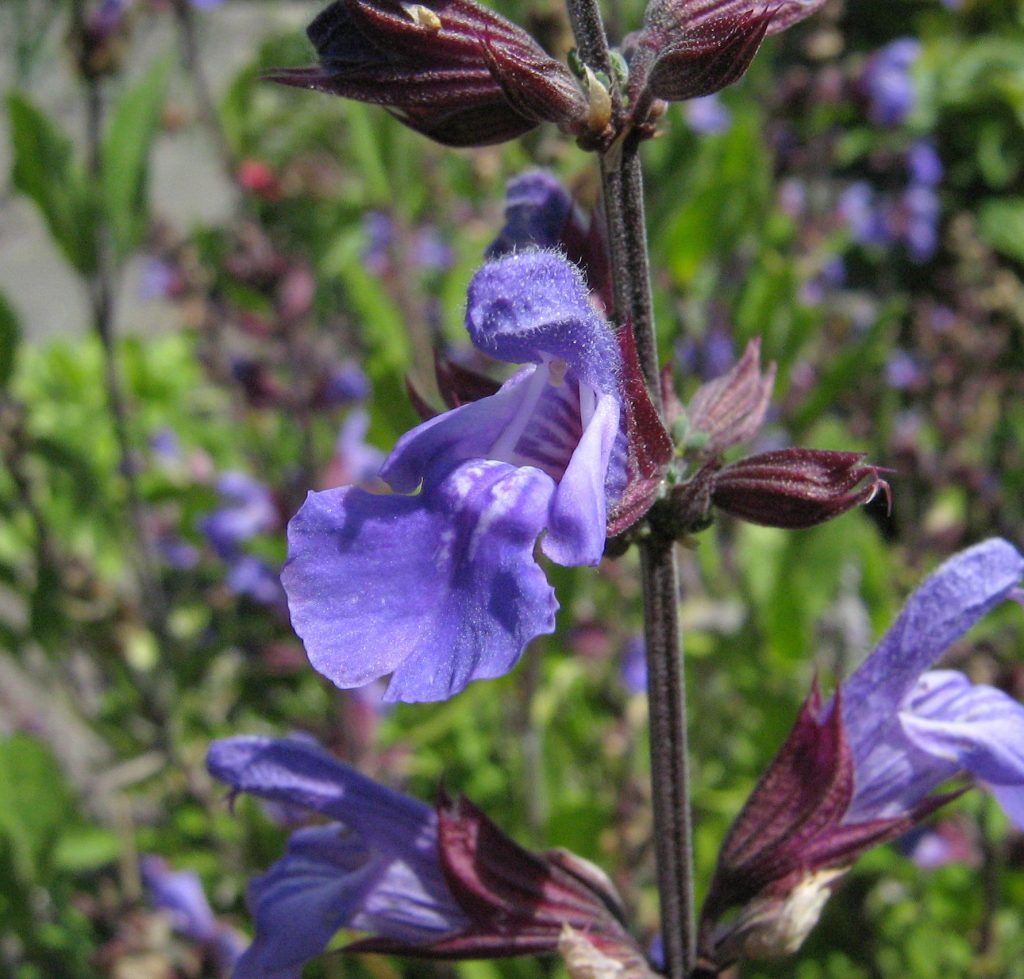
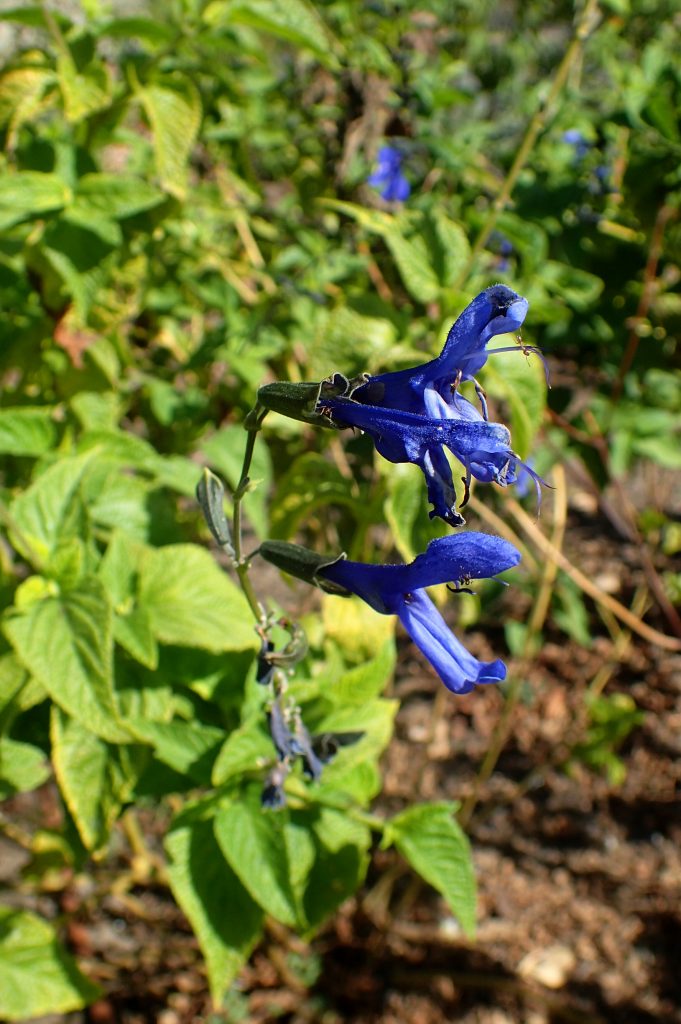
For the first time, I have three salvia (SAL-vee-uh) plants in my yard, chosen by another, planted for their blooms. I wanted to know more. And what I learned at KidsHealth and Australia’s Alcohol and Drug Foundation surprised me!
You may also know salvia as diviner’s sage, magic mint, maria pastora, sally-d, seer’s sage, and shepherdess’s herb.
Please note: what follows is readily available information. I’m absolutely not recommending any particular use of salvia.
Psychedelic Salvia
It’s an herb in the mint family that can cause brief, intense psychedelic experiences. Salvinorin A is the active ingredient in salvia divinorum. Native to the mountains of southern Mexico, salvia has a long history of use by Indigenous shamans there.
Salvinorin A affects opioid receptors in the brain. This differs from other hallucinogenic drugs like LSD and psychedelic mushrooms, which affect the brain’s levels of serotonin. As a psychedelic drug, it can affect all the senses, altering a person’s thinking, sense of time, and emotions. Psychedelics can cause a person to hallucinate, seeing or hearing things that do not exist or appear distorted.
As a drug, salvia comes as fresh green plant leaves, dried shredded leaves, or a liquid extract. Traditionally, users chewed the fresh salvia leaves or drank the extract, but now people take the drug in a variety of ways. A user can also smoke the dried leaves in a bong or mixed with tobacco as a cigarette. For sublingual absorption, a user holds the fresh leaves under the tongue.
Salvia’s effects come on quickly, sometimes in less than a minute. According to anecdotal user reports, when smoked the effects of salvia begin in 15 to 60 seconds and last for about 15 to 90 minutes. When placed under the tongue, the effects begin in around 10 to 20 minutes and last for about 30 to 120 minutes.
Savlia’s Side Effects
Psychoactive drugs affect a person’s mental state and can have varied effects depending on a person’s mood or mindset (often called the ‘set’) and/or the environment they are in (the ‘setting’). Salvia’s effects on the mind can range from mild to intense. They may be frightening, depending on how strong a dose of the drug someone takes.
(Factors affecting the effects of psychedelic drugs is too big a topic to include here, but info is readily available online.)
Common short-term effects include
- Hallucinations and changes in visual perception
- Uncontrolled laughter
- Mood and emotional swings
- Difficulty concentrating
- Sense of detachment from self and reality (not being able to tell the difference between what’s real and what’s imaginary)
- Dizziness and lightheadedness
- Lack of coordination
- Slurred speech
- Amnesia
- Loss of energy (higher doses can cause sedation)
- Pain relief
- Confusion
- Delusion
- Feelings of impending doom
- Increased appreciation of music
- Uncontrolled body movements
- Anxiety
- Restlessness
- Increased body temperature
- Time distortion
Some studies suggest that, over time, salvia use may contribute to dysphoria, which is characterized by feelings of depression, discontent, and restlessness.
Smoking salvia over a long period of time can lead to breathing trouble and other health problems.
Because the drug has such dramatic psychological effects, it can seriously impair coordination and perceptions of reality; people under its influence expose themselves to a substantial risk of injury or accidental death.
Salvia and the Law
In many areas, salvia is perfectly legal and widely available. Stores sell it as a tincture or tea in some countries, or even as commercially extracted products.
However, salvia is illegal in a number of foreign countries and in many American states. Salvia is a schedule 9 drug. Federal and state laws provide penalties for possessing, using, making, selling, importing or exporting, or driving under the influence of salvia. Possession or use of salvia in states where it is illegal is punishable by fines and jail time.
This last bit gave me an adrenaline rush. But common sense soon surfaced: a garden center wasn’t likely to be selling salvia divinorum. Nevertheless, I felt compelled to find out just what kind of salvia I have. As best I can determine, it is salvia coerulea.
Salvia’s Other Uses
Most salvias are considered non-toxic to people of any age. Many ornamental varieties have a noxious taste, but there are no known toxic qualities when consumed by humans. (In large quantities, salvia can be toxic to dogs, causing symptoms like vomiting, depression, and breathing difficulties.) So, although ornamental salvias are not poisonous, they’re nothing you’d want to put in soup.
The edible salvias are usually referred to as sage, like the Salvia officinalis used to flavor roasted chicken and turkey. In fact, there are several edible varieties that are used in everyday seasonings.
Sage’s leaves are very pungent when raw, which is why most chefs recommend cooking them before eating. However, the flowers are reputed to have a delicate taste that makes a nice garnish in salads or sauces. They are great for the pollinators too!
According to WebMD, sage might help with chemical imbalances in the brain that cause problems with memory and thinking skills. It might also change how the body uses insulin and sugar.
People commonly use sage for memory and thinking skills, high cholesterol, and symptoms of menopause. Some people also use it for pain after surgery or to treat lung cancer, sore throat, sunburn, and many other conditions, but there is no good scientific evidence to support these uses.
Bottom Line: Know your salvia and use accordingly!