It’s the time of year when many—most?—people would like to have a bit more money. Or a lot. Besides taking another job, selling their souls to corporate overlords, hustling for more tips, or panhandling, what are people doing?
There’s Always Selling Something
Lots of people sell online, everything from “pre-owned” clothes to collectibles of all sorts (think depression era glass or carved wooden pigs).
Selling Parts of Yourself
Of course, your first thought would probably be for selling items you’ve found or made. But you might start a bit closer to home.
- More personally, if you have good hair, you could sell that. Estimates suggest that several million people worldwide participate in hair selling annually, but exact numbers vary. But the human hair market, which includes hair extensions, wigs, and other hair products, is a multi-billion-dollar industry.
- Really personally, you could sell spare organs.
- Although selling human organs is illegal in the U.S. and most other countries, some estimates indicate that trafficked organs account for up to 10% of organ transplants performed around the world.
- Kidneys, lungs, and liver come to mind. Humans can live with one kidney or one lung, and a healthy liver will regenerate from the part remaining after a transplant.
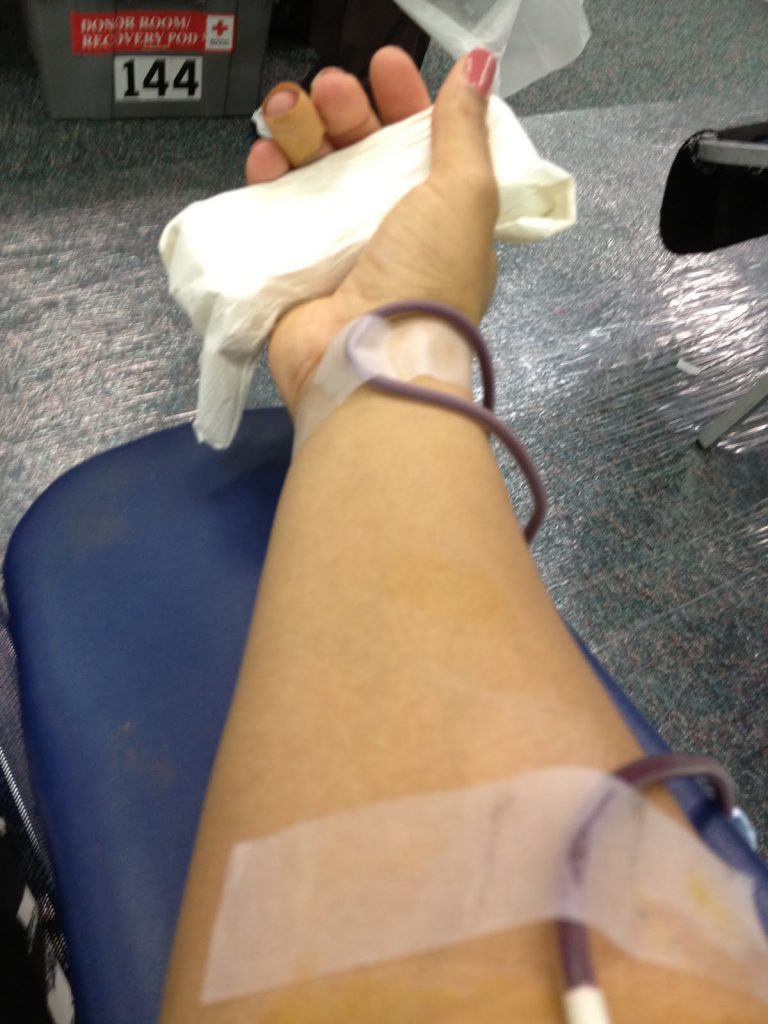
- Sell your plasma ($150-700/mo according to online sources).
- Sell sperm to a sperm bank
- “Rent” your womb as a surrogate mother
- With no medical intervention, you could sell feet or hand images, posting pictures on sites like Instafeet or Feetify
Turn Trash into Treasure

It’s amazing what people throw away!
- Haunt the neighborhood on trash collecting day or visit dumps. Salvage sellable items, clean, and resell.
- If you are artsy/crafty – turn found items into works of art and sell them at local fairs, etc.
- If you garden, sell plant cuttings, cullings, and seedlings.
- Collect cans and bottles and sell to a recycling center.
- Sell cockroaches or crickets to pet stores as food for larger animals.
- Check the change in your pocket for rare coins that might be worth more than their face value.
Essentially, if you have it, you can (try to) sell it.
Sell Your Services
If you don’t have things to sell, you might be able to sell your time and skills.
Talent Required
- This time of year, help people decorate for Christmas (or do the whole job).
- Help with course materials via OneClass
- Participate in online mock juries
- Beta test video games, phone apps, and computer programs
- Act as a Notary Public (for spending cash, it won’t pay your bills)
- Substitute as a teacher at local schools
- If you are mechanically inclined, you could hire out your handyman services
- Create websites for independent businesses or freelancers
- Be a photographer or videographer for weddings and parties
- Work temporary gigs for events, such as catering, DJ-ing, set-up and break-down, or security
- Be a professional hugger
- In CA and NYC, you could earn over $150/hour!
- Phone sex operator
- Model for art classes
- Referee seasonal sports—if you have the skill and stamina! (And the patience to stand up to upset players or coaches)
Time Required
Even if you feel you have no marketable skills, there are still ways to make a quick buck.
- Be a “line sitter”
- When there’s a high demand ticketed event, go to the venue and offer to wait in line for someone—for whatever fee the traffic will bear.

- Take drugs!
- Participate in paid clinical trials for pharmaceuticals or other treatments. If you’re relatively healthy and not taking med/drugs, you can qualify for some drug trials. You’ll have to review them carefully because some things you just don’t want to mess with while others are relatively similar to drug trials.
- Volunteer for testing medical devices/smartwatches that measure blood pressure and/or blood oxygen.
- Each session generally lasts 60-90 minutes, could pay hundreds of dollars, and only requires giving a small amount of blood. Participation is typically limited to 2x per month.
- Dog/cat/house sitting
- If you stay at peoples’ houses with their animals, you could be paid more, up to $80/night.
- Take paid surveys
- Remove lice from peoples’ heads
- Move things to/from storage units
- Garbage can cleaning—or other basic but gross jobs
- Deliver local magazine monthly (could be $150-250/month)
- Sign your kids up for research studies (e.g., get paid for letting a researcher watch your kids play)
…Other
And then there are a few options that I just couldn’t categorize:
- Watch for class-action lawsuits and join when you qualify.
- Rent out your backyard for campers.
- Found a new religion and demand tithes from all your new followers.
- Compete in interesting competitions (eating, writing, shooting basketballs, etc.) for cash prizes.
- Create community/local nude calendar. Lakeview, OR, did this to raise money for snow removal (Wall Street Journal,12/11/25).
- Sell tickets to your wedding. (Personally, I’d label this incredibly rude, gross, and financially stupid!) YouTube had a viral posting about a couple who invited 350 people to their wedding at a cost of $333 per person—including family! Only 60 people attended.
- Closely related: The Wall Street Journal (again,12/9/25) featured an article, The Lavish Weddings Where Crashers Are Welcome—for a Fee. Apparently there is a website that invites tourists (or others) to attend an Indian wedding, $150 for one day, $250 for multi-day celebrations.
Check out this Buzzfeed article for more suggestions and personal stories.
Bottom Line: Where there’s a will, there’s a way! Search online for novel ideas that suit your situation and inclinations.