Ever wonder about the safety of the food you put in your mouth or serve to your guests? It should be fine, actually. There are multiple government agencies charged with seeing to it.
Specifically, There are Three US Agencies Dealing With Food Safety
U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
The FDA is charged with protecting public health. They make sure that foods are safe, wholesome, sanitary and properly labeled. Safety and proper labeling of cosmetics and dietary supplements also fall under FDA oversight.
FDA standards and inspections cover both human and veterinary drugs, vaccines, biological products, and medical devices, ensuring they are safe and effective. This includes tobacco products.
The FDA also protects the public from electronic radiation.
Food Safety and Inspection Service (FSIS)
As part of the US Department of Agriculture, the FSIS, rather than the FDA, has jurisdiction over most meat and egg products sold in the US. From their website, “FSIS protects the public’s health by ensuring that meat, poultry and egg products are safe, wholesome and properly labeled.” The FSIS does this in part by requiring any producer of meat or eggs to follow a Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) system.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
Somewhat surprisingly, the CDC leads federal efforts to gather data on food-borne illnesses, investigate food-borne illnesses and outbreaks, and monitor the effectiveness of prevention and control efforts in reducing food-borne illnesses. The CDC also plays a key role in building state and local health department epidemiology, laboratory, and environmental health capacity to support food-borne disease surveillance and outbreak response.
So, How Effective are These Safety Measures?
According to the FDA, Americans suffer approximately 48 million cases of food poisoning every year. The CDC estimates that each year 1 in 6 Americans get sick from contaminated food or beverages and 3,000 die from food borne illness. The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) estimates that food-borne illnesses cost the United States more than $15.6 billion each year.
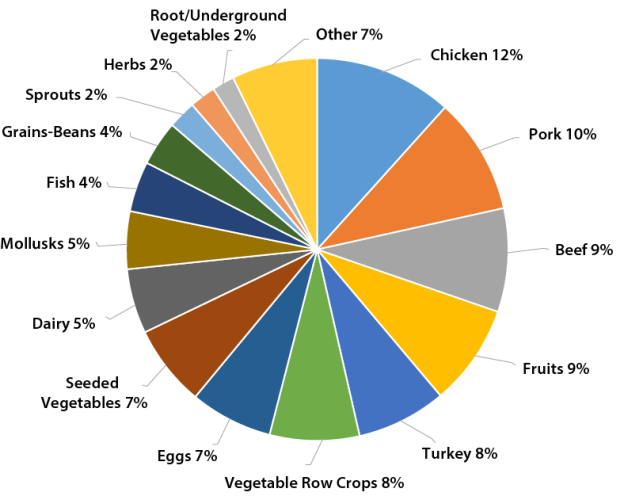
Top 15 Foods That Caused Outbreak-Associated Illnesses, 2009–2018*
- *Vegetable row crops (e.g., leafy vegetables); seeded vegetables (e.g., cucumbers); mollusks (e.g., oysters); root/underground vegetables (e.g., carrots, potatoes)
- *Unpasteurized dairy products accounted for 80% of outbreak-associated illnesses linked to dairy. Pasteurized dairy products accounted for 10%, and pasteurization status was unknown for 9%.
- *Other = foods that don’t fit in the top 15 categories and other federally regulated items such as alcohol, coffee, other beverages, ice, condiments, and dietary supplements.
- **Total of percentages does not equal 100% because of rounding.
Who is Really Responsible for Food Safety?
Everywhere I looked, I had to conclude that food safety still lays largely in the hands of individual cooks and consumers.
Things to Be Aware Of
Biological hazards include bacteria, parasites, fungi, and viruses and are the main cause of food-borne illnesses. They can develop in poorly handled food or through contamination from an outside source. Ensure that all your produce has been purchased from an approved supplier. In all cases of suspected contaminated food, dispose of it immediately. And of course, that goes double for recalled items.
Chemical hazards are substances such as pesticides or machine oils. Always handle and store correctly. Keep potentially hazardous items stored separately from your food and prep area.
Physical hazards are objects which contaminate your foods such as pieces of glass or metal, toothpicks, jewelry, or hair. The majority of recalls in the food industry in the US are related to physical hazards. Keeping all foods covered in storage will help prevent physical contamination. Take care during preparation to reduce the risk of such contamination in the kitchen.
The Three Main Sources of “Food Poisoning”
1) Time and temperature hazards result from improper cooking, holding, cooling, and reheating of food, leading to the growth of pathogens.
- Do not leave cooked food at room temperature for more than 2 hours
- Promptly refrigerate all cooked and perishable food (preferably below 5°C)
- Keep cooked food piping hot (more than 60°C) prior to serving
- Do not store food too long in the refrigerator
- Do not thaw frozen food at room temperature
- Know the degree of doneness needed for various foods, especially meat, fish, and poultry
2) Cross contamination occurs when you mix cooked and uncooked food, especially raw meat or fish.
- Assign different containers for the preparation of each kind of food
- Avoid un-sanitized surfaces, utensils and equipment at all stages of food preparation
3) Poor personal hygiene is a common culprit that’s easily avoidable by following these rules:
- Wash and sanitize hands properly between tasks and whenever they get dirty
- Wear single-use gloves while preparing or serving ready-to-eat food
- Clean and trim nails
- Bathe or shower daily
- Keep hair neatly combed, with long hair tied back
- Wear a hair net or cap and apron at all times
- Cover wounds at all times and refrain from handling food with open wounds
- Stay away from the kitchen when sick and consult a doctor as to when it is safe to return
- Remove jewelry before working
Okay, so individually each of these is easy to do. But how many people actually do all of these things all the time?
Bottom Line: It’s surprising that only 1 person in 6 suffers from food-borne illnesses each year.