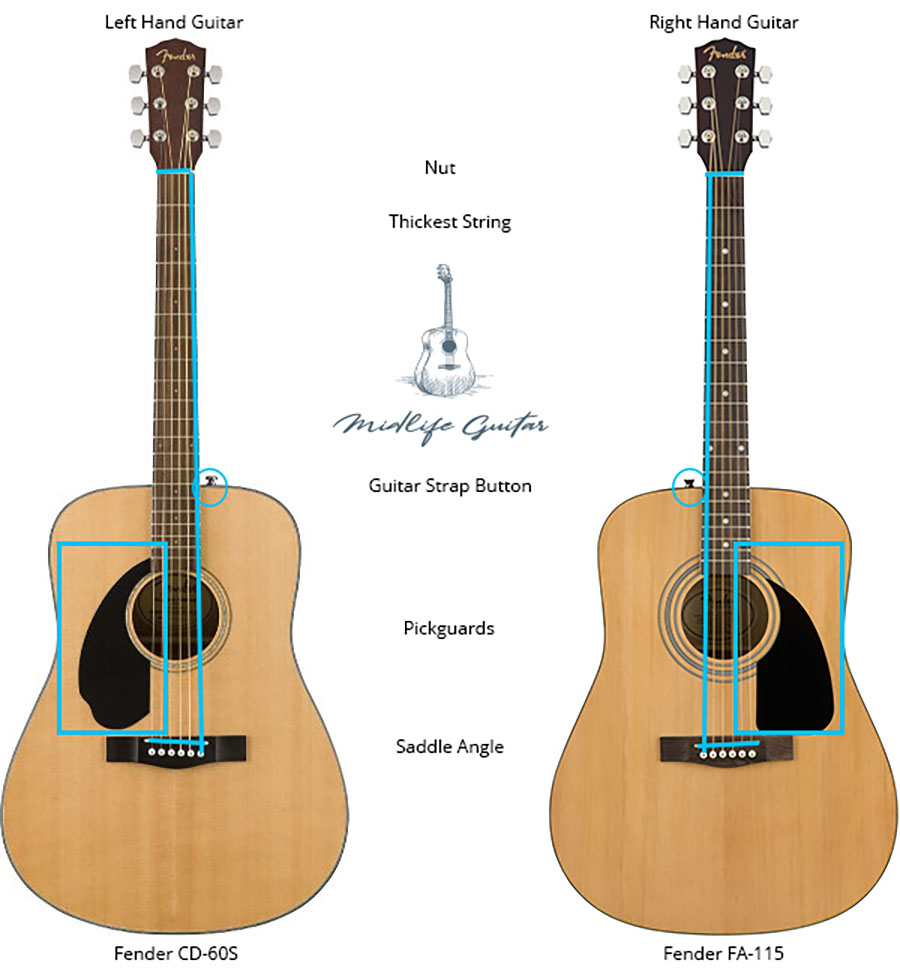
All writers should seriously consider including one or more lefties among their cast of characters – think of the possibilities! Let’s begin with ways being left-handed in and of itself creates obstacles for the leftie.

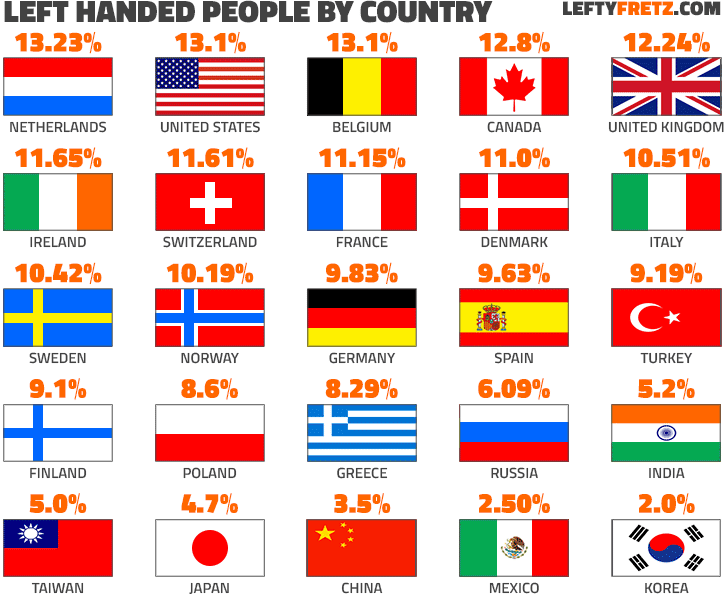
By definition, a left-handed person is in the minority: with no overt effort to control handedness, lefties make up only 10% of the population today (9% of females, 11% of males). There is evidence that 500,000 year ago, neanderthals were characterized by this 90/10 split. Simply living in a right-handed world is a challenge. Consider the number of things that are made to be used right-handed, from scissors to guitars to golf clubs. Yes, special implements are available, but that is just the point—they are “special,” and often more expensive. In some places, and at some times, special accommodations aren’t even available.
Writers Note: Any right-handed implement being used by a leftie could make a nice scene, and the way the leftie copes would clearly illuminate the leftie’s character.
Biases Against Lefties

- “Right” phrases for positive things (such as right answer, right-hand man) vs. “left” phrases for things that are clumsy or bad (e.g., two left feet or a left-handed compliment).
- Because the left hemisphere of the brain (which controls the right side of the body) is responsible for words, in almost every language the words for the right side of the body are positive and for the left side are negative.
- In English, the direction “right” also means correct or proper.
- In languages derived from Latin, left also means unlucky; sinister means evil.
- In French, gauche means left, awkward, and clumsy; droit(e) means right, straight, as well as law.
- In Ghana, a person can’t point with a left hand because the left hand is reserved for dirty things.
- In some Islamic cultures, people are said to step into the mosque with the right foot, into the toilet with the left.

- Only the right hand can be used for eating in most cultures where eating with bare hands is the norm.
- Across cultures, words with more letters on the right side of the keyboard are rated more positively than average; words with more left side letters were rated more negatively. Since 1990, names with more right-side letters are wildly more popular.
- Most religions have a strong bias for the right hand, particularly in Christian cultures:
- The faithful sit at the Right Hand of God.
- Black magic and Satanism are often referred to as the Left-Hand Path.
- “And he shall separate them one from another, as a shepherd divideth his sheep from the goats. And he shall set the sheep on his right, but the goats on his left.” Matthew 25: 32–33
- When asked to judge two alien creatures side-by-side on the page, right-handers attributed more positive to the one on the right, while lefties were more positive toward the one on the left (attribution of honest, intelligent, attractiveness).
- Lefties can learn to behave like right-handed people, and some cultures and periods in history have pushed strongly to suppress left-handedness.
Writer questions: How does your leftie cope with these biases on a daily basis? What if a leftie from a more accepting culture finds him/ herself in a stricter culture, and had to learn to write right-handed, and not hand anything to someone with the left hand?
The Downside of Left-Handedness
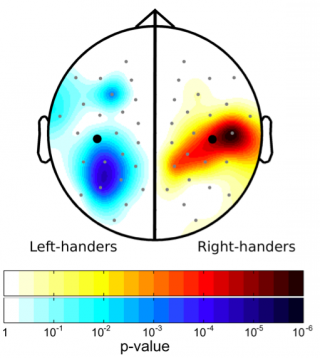
- Mental illness is more common in left-handed people.
- Lefties have a higher risk of psychosis. Lefties make up 20% or more of people diagnosed.
- Lefties make up 40% of people diagnosed as schizophrenic.
- Scientists have also found an increased risk for autism, ADHD, and dyslexia.
- Lefties are more affected by fear, often showing subtle behaviors like people with PTSD.
- Lefties are more prone to having negative emotions, such as anger.
- Lefties seem to have a harder time processing their feelings.
- Lefties report feeling more inhibited, shy, and embarrassed.
- For mood disorders, such as depression and bipolar disease, lefties make up 11%, close to their proportion in the general population.

- Left-handedness is positively correlated with lower-birth-weight and complications.
- 40% of children with cerebral palsy were left-handed.
- Lefties are more likely to break bones.
- Lefties are more likely to have heart disease and to die earlier as a result.
- For women
- Left-handedness is associated with a 62% increased risk for Parkinson’s disease.
- A higher risk of developing multiple sclerosis.
- Lefties have a higher risk of breast cancer, especially in post-menopausal women.
- Paraphiliacs (exhibiting atypical sexual interests, typically involving extreme or dangerous activities) have a higher rate of left-handedness.
- Greater rates of left-handedness have been documented for pedophiles.
- Overall lefties salaries are 10% lower on average than right-handers. (Among the college educated, lefties earned 10-15% more than their right-handed colleagues.)
Writers: choose the psychological or health issue your leftie has(to) overcome.

The Upside of Left-Handedness

- Lefties are more likely to develop some measure of dexterity in their non-dominant hand, most likely a result of years using tools designed for righties.
- Lefties have a lower rate of arthritis.
- Lefties have a lower rate of ulcers.
- Lefties are better at divergent thinking, which generating ideas that explores many possible solutions.
- Lefties tend to be drawn to careers in the arts, music, sports, and information-technology fields, and are often successful.
- A slightly larger proportion of lefties are especially gifted in music and math.

- Lefties have an advantage in hand-to-hand combat, analogous to throwing a curveball.
- Lefties have an advantage in sports that involve aiming at a target, and are over-represented in baseball, tennis, table tennis, badminton, fencing, cricket, and boxing.
- Some cultures have historically accepted or even revered left-handed individuals:
- The Incas positively regarded left-handed individuals as people who possessed special spiritual abilities.
- In Buddhism, the natural persuasion to use the left hand implied wisdom, according to it’s teachings.
- In early Russia, “levsha” (left-hander) became a common noun for a skilled craftsman of status.
- Women who hold their infants in their right arm (presumably to leave their left hand free for fine-motor skills) are less likely to suffer from post-partum depression.
Writers: At last! Ways your leftie might thrive.

Also Related to Handedness—or Not

- Immune system disorders are not more common for lefties.
- The research on handedness and homosexuality is not consistent.
- A child’s dominant hand is clear by age 3 or 4.
- Genetic males with female gender identities were more than twice as likely to be left handed than the control group
- Lefties drink more
- But they are no more prone to alcoholism.
- How speech is heard:
- Right-handed people like rapidly-changing sounds like consonants;
- Lefties hear slowly-changing sounds like syllables or intonation better.
- People use their non-dominant hand for negative gestures
- Handedness is a combination of genetics, biology, and environment; although left-handedness does tend to run in families, but a left-handed identical twin’s twin is right-handed about 30% of the time.
- Overall, people gesture more with their dominant hand, especially when saying something positive.

- People attack with their dominant hands, defend with the other.
- Lefties are biased in favor of candidates on the left side of the ballot. (Everyone is biased in favor of people listed near the top of the ballot.)
- Four of the last seven U.S. presidents were left-handed (Obama, Clinton, George H.W. Bush, and Ford); earlier, Garfield and Truman were lefties, and maybe Reagan was born a leftie but made into a right-hander. Info isn’t available for earlier presidents due to widespread efforts to suppress left-handedness.

Writers: Some of this info might help your hero/ine leftie in a fight, or it could just make for and interesting behavioral quirk.

Not addressed in this blog: There is a lot of research on handedness and brain lateralization which I haven’t touched on. I focused instead on observables and emotions that might be useful to writers.
BOTTOM LINE FOR WRITERS: a left-handed character could be a gold mine. Start prospecting!
AND LEFTIES HAVE THEIR OWN DAY: AUGUST 13 IS INTERNATIONAL LEFT-HANDERS DAY. Since 1992, it is a celebration of sinistrality—i.e., left-handedness! Mark your calendar for 2020.