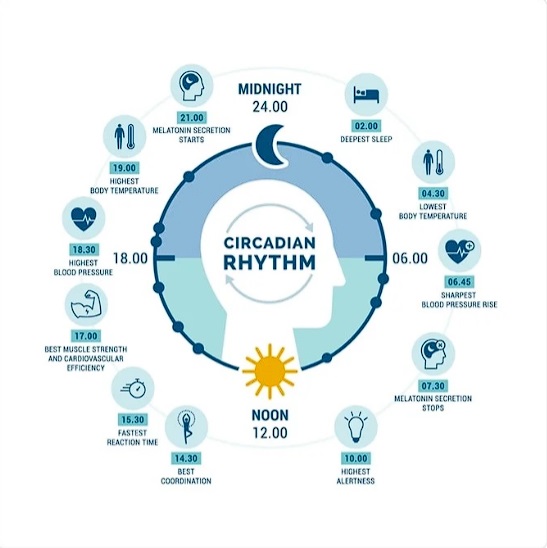
Circadian rhythms are the physical, mental, and behavioral changes an organism experiences over a 24-hour cycle. The word stems from the Latin “circum” (approximately) and “diem” (day). Light and dark have the biggest influence on circadian rhythms, but food intake, stress, physical activity, social environment, and temperature also affect them. Most living things have circadian rhythms. In humans, nearly every tissue and organ has its own circadian rhythm—which is why I’m talking about your body’s clocks, plural—and collectively they are tuned to the daily cycle of day and night.
Circadian rhythms influence many functions, such as:
- Sleep patterns
- Hormone release
- Appetite and digestion
- Temperature
How Long is a Circadian Rhythm?
Early research suggested that most people preferred a day closer to 25 hours when isolated from external stimuli like daylight and timekeeping. However, this research was faulty because it failed to shield the participants from artificial light. Although subjects were shielded from time cues (like clocks) and daylight, the researchers were not aware of the phase-delaying effects of indoor electric lights. The subjects were allowed to turn on light when they were awake and to turn it off when they wanted to sleep. Electric light in the evening delayed their circadian phase.
More recent research has shown some more specific things:
- Adults have a built-in day, which averages about 24 hours
- Indoor lighting does affect circadian rhythms
- Most people attain their best-quality sleep during their chronotype-determined sleep periods
A study by Czeisler et al. at Harvard found the range for normal, healthy adults of all ages to be quite narrow: 24 hours and 11 minutes ± 16 minutes.
In normal subjects in the real world, the body’s “clocks” are reset, primarily by exposure to light, so that they follow the 24-hour light/dark cycle of the Earth’s rotation.
When the Body’s Clocks Break
Circadian rhythms can fall out of sync with the outside world because of factors in the human body or environment. For example
- Variants of certain genes can affect the proteins that control biological clocks
- Neurological diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease, can disrupt circadian rhythms, causing poor sleep quality and changes in symptoms from day to night
- Light from electronic devices at night can confuse biological clocks
Drowsiness, poor coordination, and difficulty with learning and focus may occur when circadian rhythms fall out of sync short term.
Working swing shifts can also disrupt the body’s clocks. Forcing oneself to wake up and go to sleep at varying intervals from one day to the next leaves the body confused. Shift Work Sleep Disorder (SWSD) can cause trouble falling asleep, staying asleep, sleeping deeply, and waking up. People who work as nurses, late-night retail workers, overnight hotel staff, or fire fighters (just to name a few) often experience insomnia, hypersomnia, or both.
Jet lag causes disruptions in the circadian rhythm because modern travel allows the body to cross time zones faster than the body’s clocks can adapt. Earlier methods of travel, even early air travel, were slow enough that the body could keep up with changes in sunrise and sunset times. That’s why you won’t get jet lag on a boat!
Long-term sleep loss and continually shifting circadian rhythms can increase the risks of obesity, diabetes, mood disorders, heart and blood pressure problems, and cancer, and can also worsen existing health issues.
Changes With Age
According to National Library of Medicine, Biotech Information circadian rhythms shift throughout the lifespan, peaking in lateness during adolescence and then gradually shifting back as we age. This shift mirrors the U-shape curve of happiness, which some researchers suggest may be related.
Consistent with the transition to a morning chronotype in older adult humans, the circadian phase of sleep onset and wakening advances with age, whereby older adults (mean age of 68 years) report preferred bedtimes 1 to 2 hours earlier, on average, compared with younger adults (mean age of 23
years) (National Institutes of Health (NIH).
With age, people are less able to recover and recover quickly from disruptions to our circadian clocks. Changes to the circadian rhythm are a common cause of sleep problems in older adults .
Bottom Line: Be aware of your body’s clocks and work with them, not against them, to maximize your physical and mental well-being.