In this last blog of the giving thanks series, I’ll focus mainly on the Americas and nearby islands, but with a P.S. related to American history.
Indigenous North Americans
Centuries before Europeans landed at Plymouth Rock or Newfoundland, agricultural communities along the Eastern seaboard held annual harvest celebrations every year. Though the details varied among tribes and climates, all involved giving thanks for a successful harvest and making preparations for the coming winter.
People preserved food they’d grown or gathered, such as cattails, corn, pawpaws, pumpkins, and fish. They also repaired and reinforced structures to face the coming winter weather. Festivities included music, dancing, and games.
Puerto Rico
After Puerto Rico became a territory of the United States in the late 19th century, its residents adopted many of the traditions of the American holiday, blending them with Puerto Rican culture. The focus is on a Thanksgiving meal that fuses flavors from both cuisines, with large family gatherings. Puerto Ricans celebrate Thanksgiving on the same day as Americans (the fourth Thursday in November).
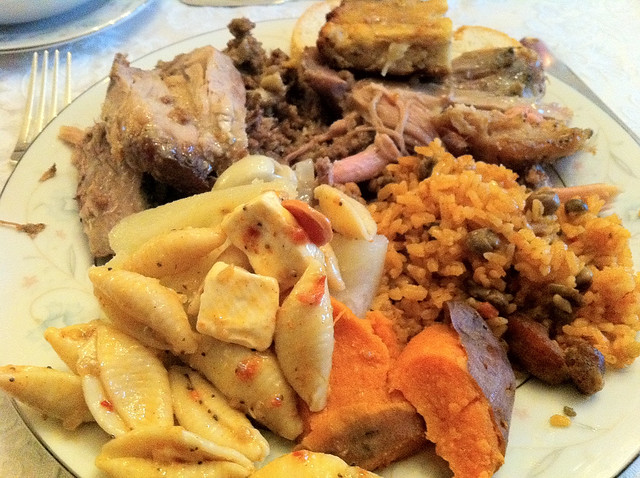
But Puerto Ricans have put their own twist on the traditional Thanksgiving Day feast: there’s usually turkey—whether a roasted, seasoned pavochón or a turkey stuffed with mofongo (a mashed plantain dish)—but roast pork is also often on the menu, accompanied with more plantains, rice, and beans. Many Puerto Ricans embrace the same Black Friday shopping frenzy on the following day, and Christmas preparations also start around then.
Canadian Thanksgiving
Like its US counterpart, the first European Canadian Thanksgiving brought Canadian pilgrims together to give thanks for their new lives in the New World. This celebration took place in 1578, when English explorer Martin Frobisher held a feast in what’s now Nunavut to give thanks for the safety of his fleet. This feast actually pre-dated the first American Thanksgiving. (Historians believe that the first American Thanksgiving took place in 1621, over 40 years later.)
Today, Canadian Thanksgiving takes place on the second Monday of October. (First officially recognized in 1879 (November 6), it was moved to the second Monday in October in 1957.) Much like the U.S., it’s a time for gratitude, reflection, and delicious food shared with loved ones.
While Indigenous peoples had long celebrated harvest festivals, it was Loyalists who moved to Canada from the American colonies during the Revolutionary War who introduced turkey, along with some of the other customs from the American Thanksgiving we’re familiar with today. Pumpkin pie, stuffing, and sweet potatoes would certainly be familiar, though traditional poutine (french fries topped with cheese curds and gravy) sometimes appears as well.
Of course, Canada’s Thanksgiving comes with a Canadian twist—think butter tarts and the Canadian Football League’s Thanksgiving Day Classic.
Mexico: Día de Acción de Gracias
With a regional twist on traditional American Thanksgiving dishes, such as mole poblano and tamales, apple pie empanadas and turkey enchiladas, many Mexicans embrace the spirit of giving thanks while spending time with family and friends. Because Mexico is so close to the United States climate-wise, Día de Acción de Gracias usually occurs on the same day as American Thanksgiving.
While not widely celebrated throughout Mexico, some cities host small community events and tourists-targeted activities, while others observe religious services and harvest celebrations. Traditions may include Mexican elements such as piñatas or pan de muerto, reflecting a non-traditional but increasingly observed blend of customs. As more families travel to and from Mexico during the holiday season, Thanksgiving observances are spreading to more parts of the country.
Brazil: Dia de Ação de Graças
Brazilian Thanksgiving (Dia de Ação de Graças in Portuguese) follows the American tradition of a harvest feast on the fourth Thursday in November. It became a national Brazilian holiday in 1949 as a way to unify the Brazilian people. The Brazilian ambassador to the U.S. saw Americans enjoying a day of eating delicious food and giving thanks and decided that Brazilians should do the same. It’s been an unofficial holiday ever since.
Brazil is the only country in South America that celebrates Thanksgiving.
Though still not widely celebrated in Brazil, Dia de Ação de Graças is catching on each year. A Thanksgiving feast in Brazil includes many American staples, including turkey (known as peru in Portuguese), mashed potatoes (purê de batatas), and apple pie (torta de maçã). Brazilian specialties, such as the country’s national dish, feijoada, might make an appearance as well. Besides food and family, there are parades and church services to give thanks.
Thanksgiving in Barbados
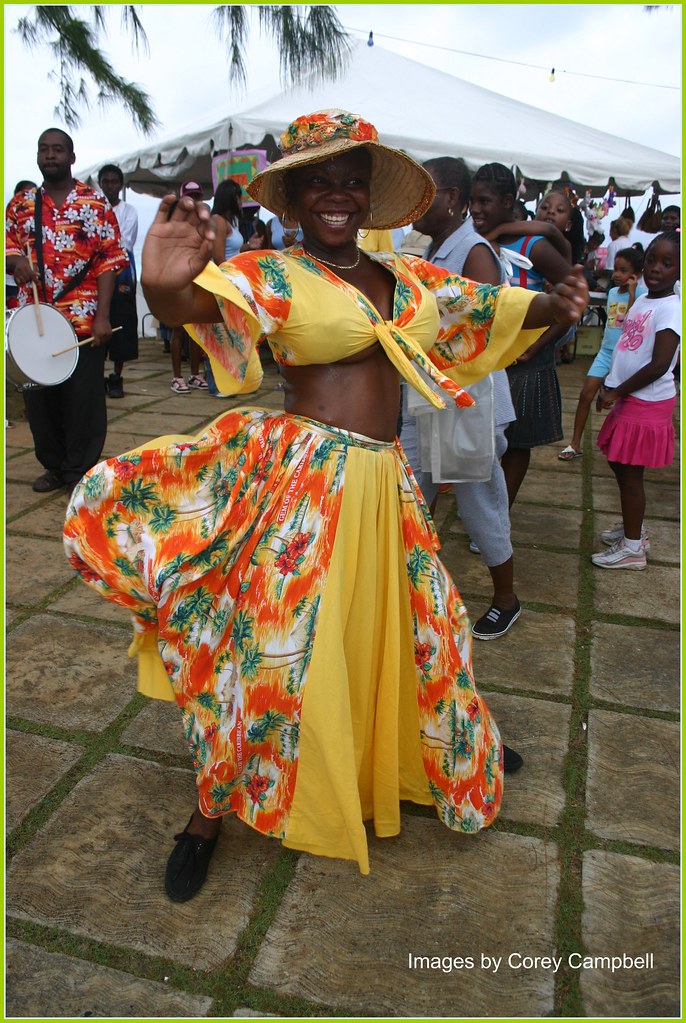
The people of Barbados celebrate Thanksgiving with a Crop Over festival at the end of the sugarcane harvest. This is typically held at the end of July through early August. This is a 300-year-old tradition that goes back to those who worked on sugarcane plantations and celebrated the harvest season. The celebrations include dancing, eating, and games.
Crop Over festivities begin with a ceremonial delivery of the Last Canes and crowning the Festival King and Queen. During Cohobblopot, Kadooment bands showcase their skills, and calypsonians perform to huge audiences. Local businesses offer their wares at the Bridgertown Market and sponsor calypso tents. Kadooment Day, the final day of the celebration, culminates in a carnival parade, with huge floats, elaborate dance troupes, and competing calypso bands.
Grenada West Indies
Every October 25, people on this West Indian island celebrate their own Thanksgiving Day, which marks the anniversary of a joint Caribbean and U.S. military invasion of Grenada in 1983. The troops’ arrival restored order after an army coup ousted and executed Maurice Bishop, Grenada’s socialist leader, and put the island under martial law.
While stationed on the West Indian island that fall, U.S. soldiers told local citizens about the upcoming American holiday and some of its traditions. To show their own gratitude, many people in towns and villages hosting the soldiers invited them to dine and celebrate with them, even surprising the soldiers with such non-native island foods as turkey, cranberry, and potatoes. Today, the Grenadian Thanksgiving features formal ceremonies of remembrance in the cities, but largely goes unmarked in more rural areas.
Liberian Thanksgiving
In the 1820s, free Blacks from American purchased Cape Mesurado and settled in the new colony of Liberia. In the 1880s, the Liberian government adopted the first Thursday in November as Thanksgiving, to express gratitude for the year’s blessings. (Unlike Thanksgiving events in other parts of the world, Liberian Thanksgiving isn’t a harvest festival; their harvests are often over by November.) Because English is the primary language of Liberia, celebrants greet each other with “Happy Thanksgiving!”
Liberian Thanksgiving combines American traditions with religious rituals to thank God for blessings from the year, including food, health, and good weather. Today, it’s a largely Christian holiday. After services, churches auction off baskets filled with local fruits like papayas and mangoes.
The typical meal consists of a bird (sometimes chicken) with plenty of spices as well as mashed cassava and other traditional West African foods like jollof rice (similar to Cajun jambalaya) or fufu (cassava dough served with meat stew).
Celebrations are lively, marked by food but also music, dancing, and a deep sense of community.
Bottom Line: As these examples attest, giving thanks isn’t the province solely of the United States. Try pursue the topic of giving thanks in Israel, Ghana, Rwanda, and any other locations that interest you.