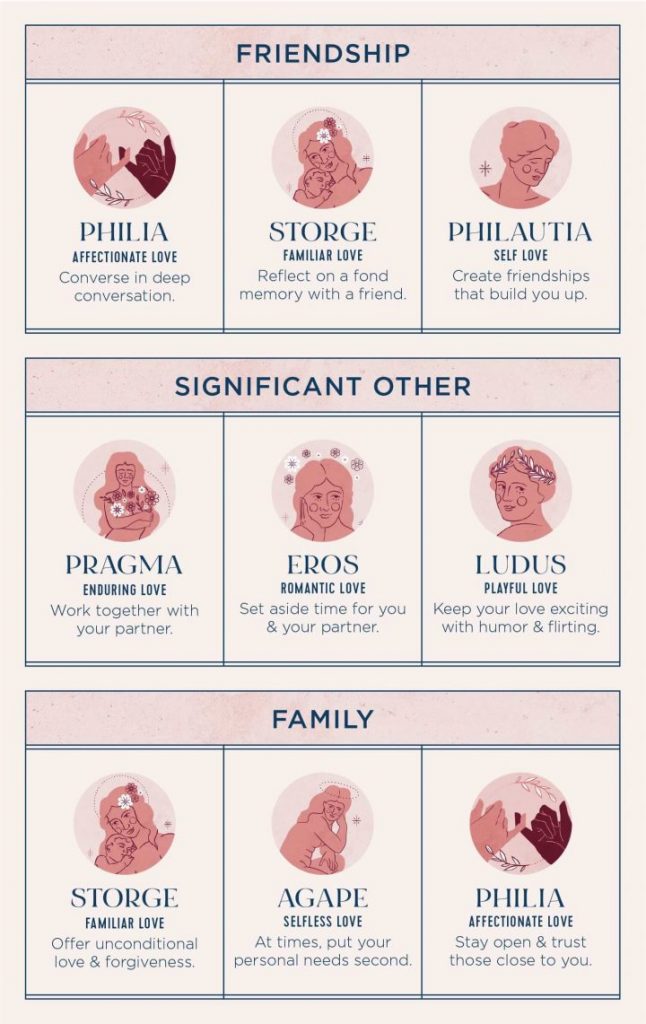
Overall, husbands in heterosexual marriages tend to be older, taller, better educated, and financially better off than their wives. This is the mating gradient: in mate selection, women marry up and men marry down. This pattern is socially and culturally approved to such an extent that often this configuration is perceived as what mates “should” be.

What Women (and Men) Want
Traditionally, members of couples are similar in age, race, class, appearance, and education. But within that common background, men tend to marry women slightly below themselves, per the marriage gradient discussed above. To determine the extent to which students were comfortable with unequal relationships, and with traditional and untraditional inequalities, 277 predominantly white, middle and upper middle class students (140 male, 137 female), between the ages of 18-23, completed an attitude questionnaire. Two hypothetical situations were presented, one in which the “spouse” was older, taller, more intelligent and richer, and a second scenario in which the “spouse” was younger, shorter, less intelligent, etc. Students rated their degree of comfort with each hypothetical spouse on a Likert-type scale and then explained their ratings. An analysis of the results showed that students were most comfortable with the traditional inequalities of the mating gradient. College men wanted women who were shorter and better looking than themselves; however, they also wanted similarity in earnings, intelligence, age, and education. Women wanted spouses who earned more, were older, better educated, and taller. (V. P. Makosky and B. K. Sholley, 1983)
When I conducted that research forty years ago, I thought that the mating gradient would be less powerful than it had been in the 1950s—but it wasn’t. And as best I can determine, it’s alive and well today.
Some maintain that the mating gradient is derived from biology: men are attracted to women who can bear their children, and women are attracted to men who can provide for them and their children.
Historically, the husband’s status determined the family’s status. And family wealth often passed to male heirs. Primogeniture laws in England required that noble titles (and sometimes estates) could only pass to male heirs, a state of affairs that caused great consternation for the Bennet sisters in Pride and Prejudice.

The growing popularity of online dating has reflected the continuation of these trends. Researchers have demonstrated that, although everyone (53% of US respondents and 44% of British respondents) seems to lie on the their dating profiles, men and women lie about different things. Women often list their age as younger, often going so far as to post heavily manipulated photos or photos of themselves when they were younger. Men are more likely to present themselves as taller, better educated, and wealthier than reality. Everyone lies about their weight or level of physical fitness.
Effects on Women
So, it may seem that women gain greater benefits from marriage than men do. But do they really?

This prescribed pattern for husbands and wives carries profound implications at a societal level. For example, higher status females have difficultly finding males of even higher status and lower status males have difficulty finding females of even lower status, as deemed suitable by the mating gradient. Times are changing, but it is still the case that the “best” women at the top of the gradient are likely to produce fewer children.
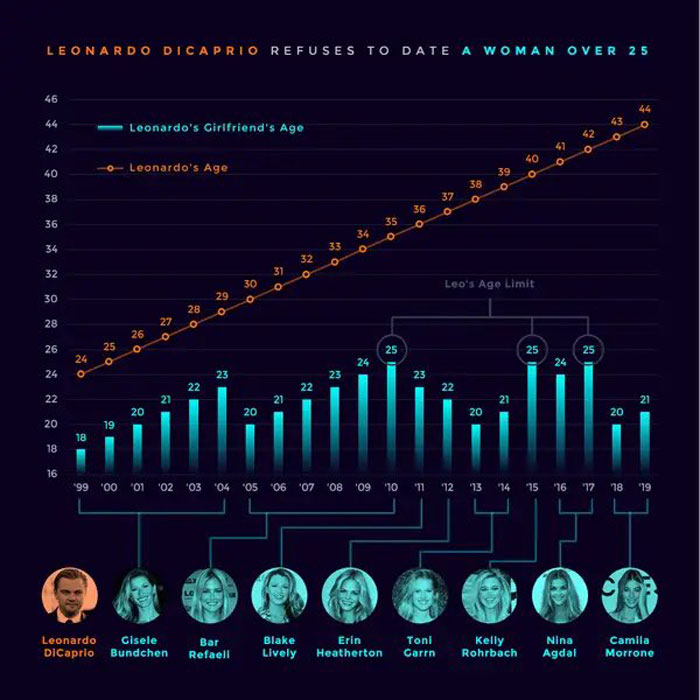
(image by Sarah Lerner)
Although changes in fertility and in mortality are contributing factors, the ubiquitous norm that husbands should be older than their wives is paramount. This mating gradient is the most significant determinant of the competition for mates as it is experienced by older unmarried women compared with older unmarried men. Some app creators have capitalized on this state by marketing online dating apps specifically tailored to older people.
Jean E. Veevers created “availability indices” to estimate the number of unmarried persons of the opposite sex potentially available for every 100 unmarried persons. For men, availability indices are low in the 20s, and they increase with advancing age to about one-to-one in their 50s. For women, access to potential grooms is highest in the 20s and decreases with advancing age until, in their 50s, there are only 50 potential grooms per 100 unmarried women. (The “Real” Marriage Squeeze: Mate Selection, Mortality, and the Mating Gradient, Jean E. Veevers, University of Victoria.)
Effects on Society
Consider the implications for women’s mental health of always being the lesser partner. Who makes decisions for the family? Whose job/work/profession takes precedence? Who has the power? At least historically, some states had laws concerning the right of domicile, such that if a wife refused to relocate with her husband, he could divorce her on grounds of desertion.
Consider the implications for men. How can a man respect his wife? Can he trust her to problem solve? To handle finances, car repair, etc., as he ages? What happens to that dynamic in the face of developing illness or disability?
Women have a significantly higher frequency of depression and anxiety in adulthood, while men have a higher prevalence of substance use disorders and antisocial behaviors. In my opinion, the roles that accompany the mating gradient contribute to these mental heath issues.
Women are more likely to internalize emotions, which typically results in withdrawal, loneliness, and depression. Men are more likely to externalize emotions, leading to aggressive, impulsive, coercive, and non-compliant behavior.
Gender inequality has a significant impact on mental health for men and women. Women and persons of marginalized genders exhibit higher levels of stress, anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder.
Bottom Line: In my opinion, each partner should be “superior” on some but not all of the mating gradient factors.