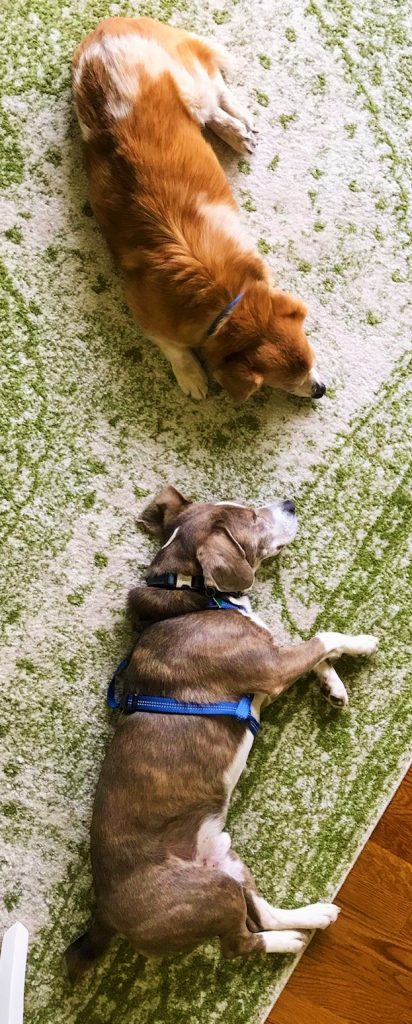
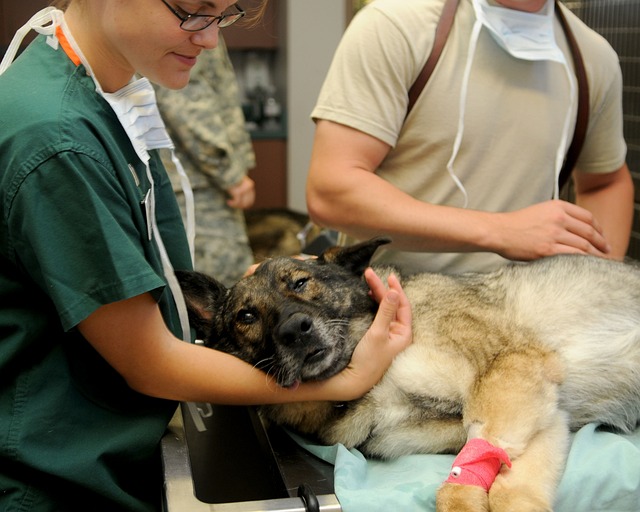
One of my daughters owns these dogs (currently and formerly) and works at the Wheat Ridge Animal Hospital in Colorado, which operates blood banks for dogs and cats. (More about cats next month!) And thus I learned about blood donor dogs.
Which Dogs Can Donate?
There’s no particular breed for blood donor dogs, but not just any dog off the street can donate. These requirements apply generally for donor dogs, not specific to Wheat Ridge:
- Be between 1 and 8 years old.*
- Weigh 50 pounds or more.**
- Be healthy (based on a complete physical exam and blood work).
- Be friendly, calm, and have a good disposition.
- Be on year-round heart worm, tick, and flea preventatives.
- Be current on Rabies and DAPP (Distemper, Adenovirus, Parvovirus, and Parainfluenza) vaccines.
- Dogs may require additional vaccines specific to a geographic location.
- Some veterinarians allow blood donor dogs with chronic medications, assessed on a case-by-case basis.
- Contact your local blood bank for a list of permitted medications.
- Not be on a raw diet due to concern for salmonella transmission via transfusion.
- Not have received a blood transfusion, or (for some programs) have no history of pregnancy.
*Retirement typically occurs on or around a pet’s 8th birthday. However, some exceptions may apply based on the discretion of a licensed veterinarian.
**Some blood banks have the ability to collect smaller units from 40-pound dogs. Contact your local blood bank regarding your pet’s enrollment.
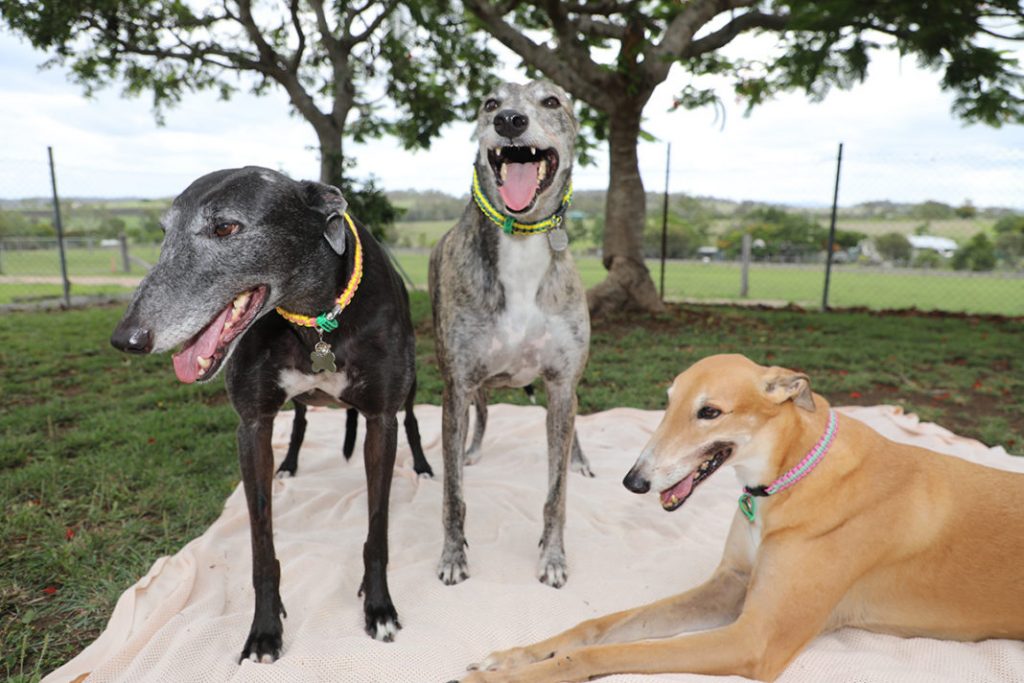
I applaud all donor dogs! I happen to especially like Yumee, Bernadette, and Bruce because they are such lovable and loving pets. Not small animals, they nevertheless think they should be lap dogs. Whenever possible, they cuddle with humans and with each other as well.
.



.
They—and donor dogs in general—love being loved on by clinic staff, with lots of belly rubs and praise. Just as humans get juice and cookies after donating, blood donor dogs often receive treats after, as well.
Although some places maintain kennels of donor dogs, it’s common for donors to be the pets of a particular practice’s staff and clients.
The Wheat Ridge bank began with a kennel of rescued greyhounds. The dogs received full veterinary treatment, and after a year as a blood donor, stood ready for adoption. When HB1146 outlawed greyhound racing in Colorado in 2014, members of the community stepped in. Today, Wheat Ridge relies on pets of employees and clients.
When a Dog Donates Blood, Exactly What Happens?
Technicians gently placed the donor on his or her side atop comfortable bedding and soothe them while cleaning and prepping the area on and around the jugular vein. A dog’s jugular vein is prominent, accessible, and generally not sensitive to the needle.
Once the technician has sterilized and, if necessary, clipped or shaved, the area, they then draw blood through a needle into a sterile collection set.
Dogs with big neck veins make drawing blood easy.
.
Donating blood does not adversely affect most dogs. Unlike humans, dogs have a mobile reservoir of red blood cells in their spleens and can replace 1/3 of the donated blood immediately. They will regenerate the rest of the blood cells within a couple of days.
Although your dog can safely give blood every 30 to 45 days, blood donor dogs typically make a donation every 60 to 90 days. Dogs weighing at least 40 pounds can safely donate a half pint of blood every 4 to 6 weeks (see above). Dogs weighing over 50 pounds typically donate a pint of blood every 8 weeks.
Bruce Lee was a super donor. He donated a pint of blood every 6-8 weeks for seven years. You can do the math! Besides being a frequent donor, he was ideal overall. He’d jump up on the table, lie quietly, and wag his tail throughout the procedure!
Because of the great need for canine blood products, most banks encourage a dog to donate at least four times a year. Most veterinarians check to ensure that donors have an adequate red blood cell concentration before drawing blood. Like with humans, canine blood banks don’t want anemic donors!
Fortunately, most dogs never need a blood transfusion, but for those that do, it can be lifesaving. Many dogs need blood transfusions for surgeries. Also, for diseases where there is ongoing blood loss or destruction of blood cells, the dog may need repeated blood transfusions.
Canine Blood Types
Researchers separate blood donor dogs into at least 13 blood groups based on antigens, and dogs can have multiple blood types simultaneously. (The existence of these antigens mean that dogs that have received blood transfusions can no longer act as canine blood donors.) Veterinarians use the dog erythrocyte antigen (DEA) system. Ideally, transfusions should be between typed and crossmatched individuals.
Fortunately, about 1 in 15 dogs have “universal” donor blood, meaning they can donate to either positive or negative recipients.
About 70% of Greyhounds are universal donors. Boxers, Irish Wolfhounds, German Shepherds, Dobermans, and Pit Bulls are other breeds more likely than average to be universal donors.



Dogs that need transfusions usually receive blood components. Laboratories separate whole blood into several useful forms; pRBCs, fresh-frozen plasma (FFP), frozen plasma for long-term storage, platelet-rich plasma (PRP), platelet concentrate, and cryoprecipitate.
Each component has multiple uses. For example:’
- RBCs (red blood cells) are used for patients with acute chronic hemorrhage, hemolysis, renal disease, and bone marrow disorders.
- FFP (plasma) contains clotting factors and albumen, and is used to treat bleeding due to anticoagulant rodenticide toxicity, liver failure, or congenital clotting deficiencies.
- Cryopreccipitate (platelets) can be used in the treatment of some hemophilia and as a topical hemostatic in surgery.
When a dog donates blood, it is rescuing three fellow canines!
There was a national shortage of canine blood for transfusions during the pandemic, and demand usually goes up during the summer. To encourage donations, sometimes clinics and communities spotlight superhero dogs. For example, the Wheat Ridge newsletter once featured Bruce Lee as a super-donor. Local media noticed and spotlighted his blood donor heroism as well!
And when not donating blood, donor dogs just do what dogs do!



.
Bottom line: Dog blood donors are always welcome! Is your pet a candidate? Find a canine blood bank near you!