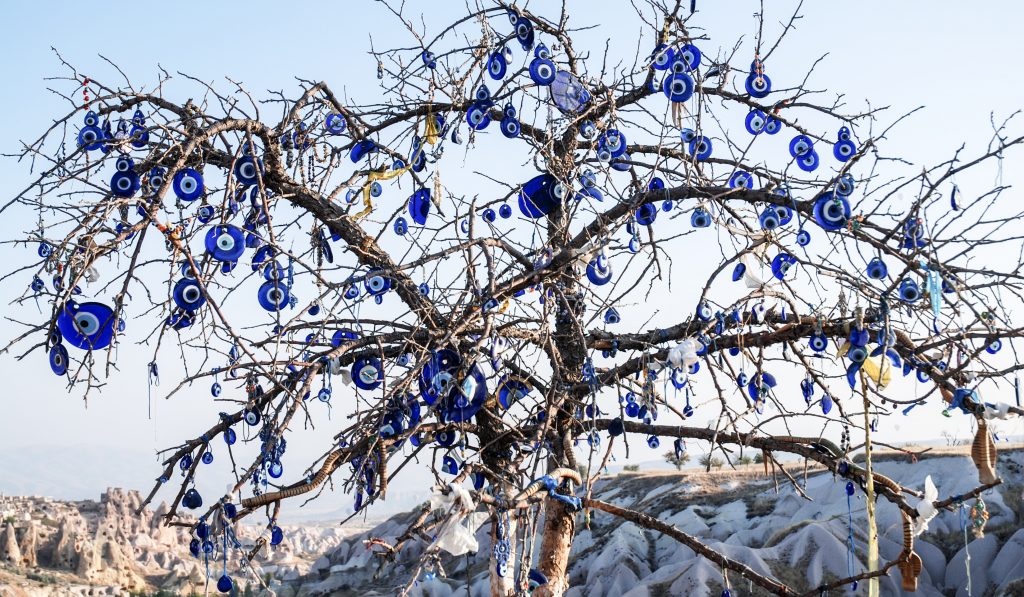
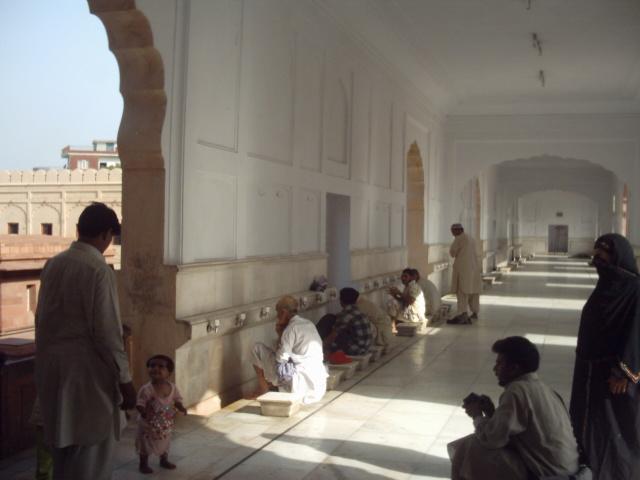
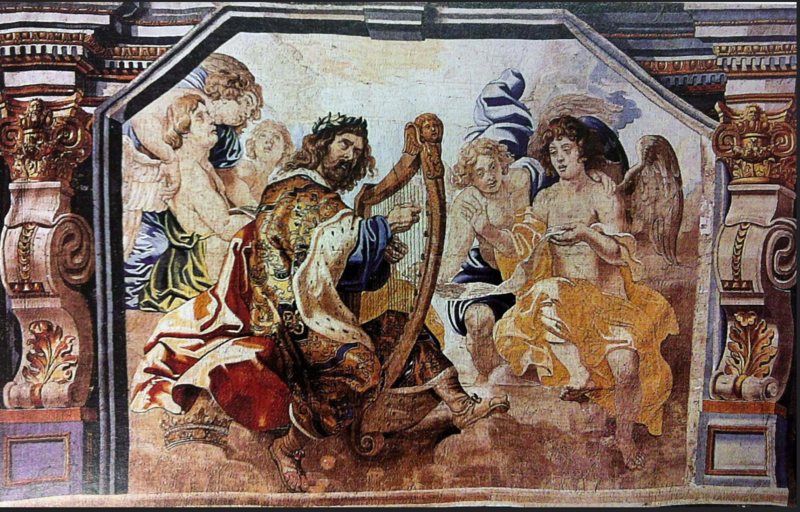
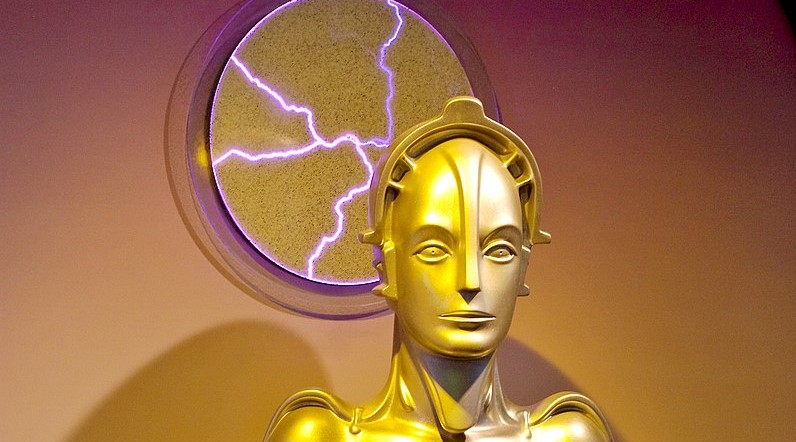
(Nazur pendants outside Cappadocia, Turkey)

“If I didn’t have bad luck, I wouldn’t have any luck at all.” How often have you heard that? When it’s better to have no luck at all, what’s a person to do?
Is it possible to change one’s luck?
Note: the following not-exhaustive lists were compiled from articles in Wikipedia, on history.com, at liveabout.com, mom.com
Warding Off Bad Luck
- Carrying a 4-leaf clover reveals fairies hiding behind flowers, allowing one to prevent the mischief they could do. Some species of clover all have four leaves, but those have no power. The powerful 4-leaf clover is a mutant of the 3-leaf clover, occurring approximately 1 in 10,000. To know you’ve found a true four-leaf clover, look for one leaflet that’s smaller than the others. If all four leaflets are the same size, you are probably looking at the wrong variety of clover.
- Lucky rabbit foot: The original legend says that the left hind foot of a rabbit that is captured in a cemetery at night can ward off evil magic. These amulets definitely do not ward off bad luck for the rabbit!
- Romans were very superstitious, and a lot of that superstition centered on reproductive organs.
- Soldiers carved phallic totems for good luck and protection from Pompeii to Hadrian’s Wall.
- According to the ancient writer Marcus Terentius Varro, Roman boys were even known to wear fascinus (winged penis) amulets around their necks to prevent harm from coming to them.
- It was once thought that giving someone an evil eye (what might be called a stink eye these days) could cause all manner of bad, from mental illness to physical ailments.
- People used evil eye talismans, or nazur (from Arabic نَظَر), to ward off the bad luck caused by these curses. Popular and beautiful evil eye talismans from Turkey use glass beads or discs with alternating blue and white circles. These are still widely in use in Turkey.
- Some cultures use a hand with an eye in its center for protection.
- Others use blue or green beads.
Attracting Good Luck
Lucky Animals
- The Chinese word for bat means “good luck.” Bats are seen as a sign of a long and healthy life. Some Chinese wear bat amulets to bring good fortune. Bats on greeting cards mean the sender is wising the recipient wellness and success.
- Bears have been revered by both Native American and Siberian cultures. They are seen as good luck because a single bear carcass can feed a family/group for a long time. They were thought to have supernatural powers of good, based on being able to hibernate through the winter. Siberians believed that the bear was an incarnation of their god.
- Goldfish are one of the eight sacred symbols of Buddha, representing fertility, abundance, and harmony. Ancient Greeks though goldfish brought good luck to marriage. Egyptians kept them in their homes “to add positivity to domestic situations.”
- Greek, Celtic, Egyptian, and East Indian people all see a bull as a powerful force. It is said to be a sign of positive things from good health to wealth. The Greeks looked upon the bull as a master of love and fertility.
- The deer is another symbol of Chinese good luck. The word for deer, “lu,” means “income.” Often the deer symbolizes luck, success, longevity and prosperity, and the hope for a long and healthy life.
- In India, the elephant is seen as a bringer of fortune and wealth.
- The frog is a good-luck symbol for many cultures that depend on rain for rich and bountiful crops. Others see frogs as a symbol of fertility, transformation and safe travel.
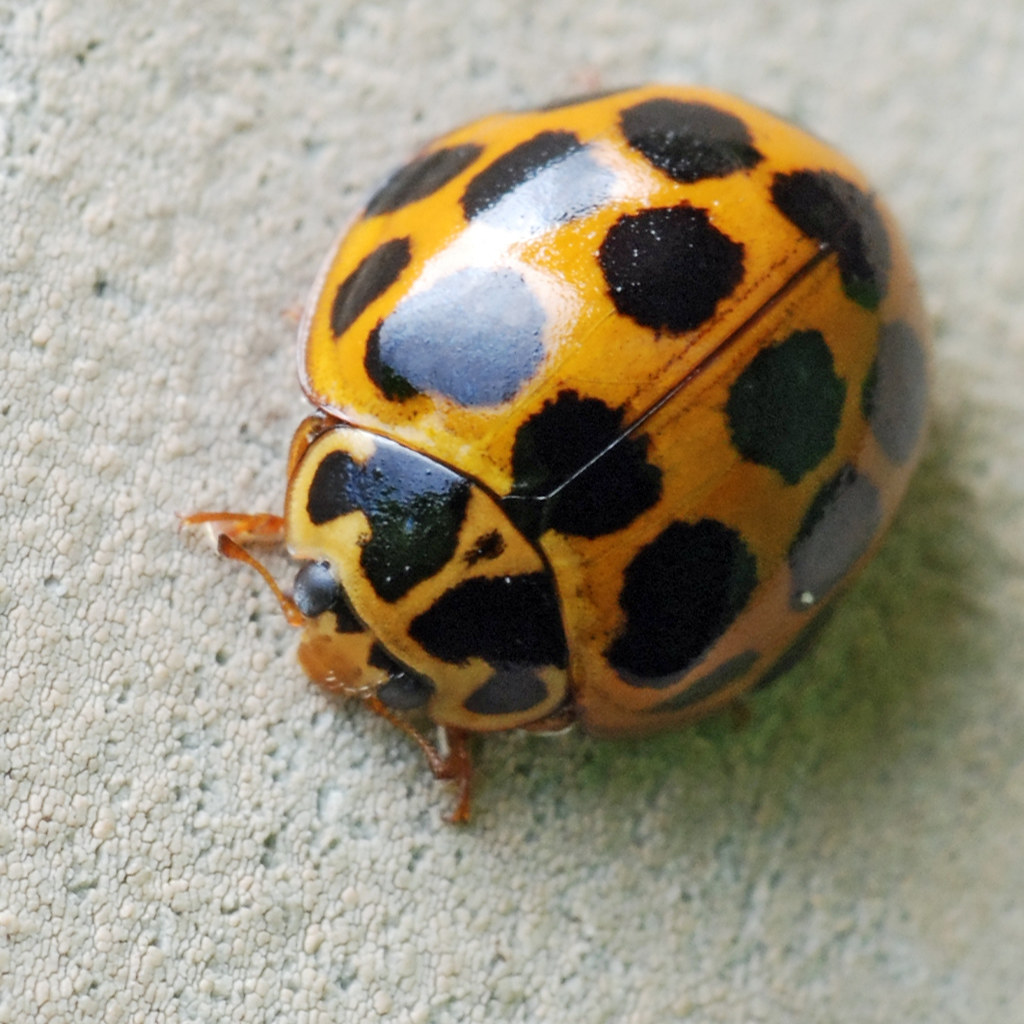
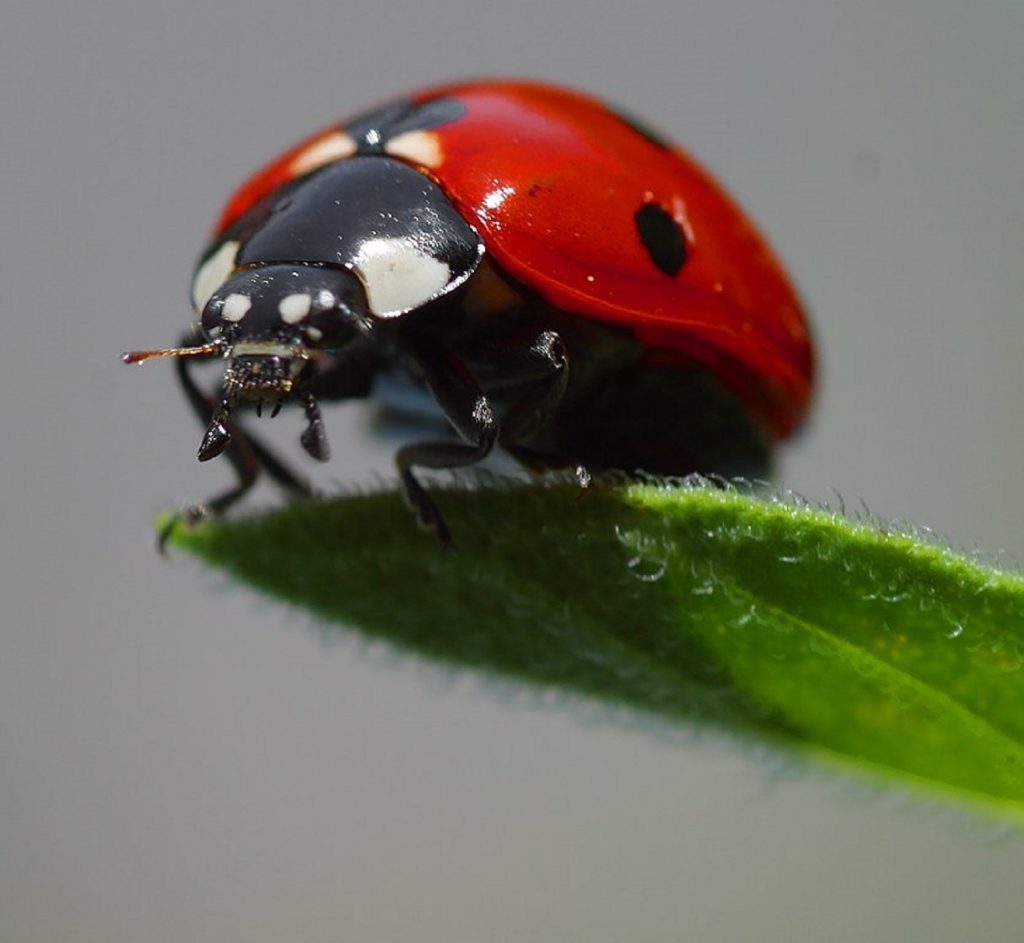
- Ladybugs: In German-speaking countries, they are literally called lucky bugs, “Glueckskaefer.” Some cultures say that if a ladybug lands on you and you don’t brush it off, your luck will improve. The deeper red their color and the more spots they have, the luckier you’ll be!
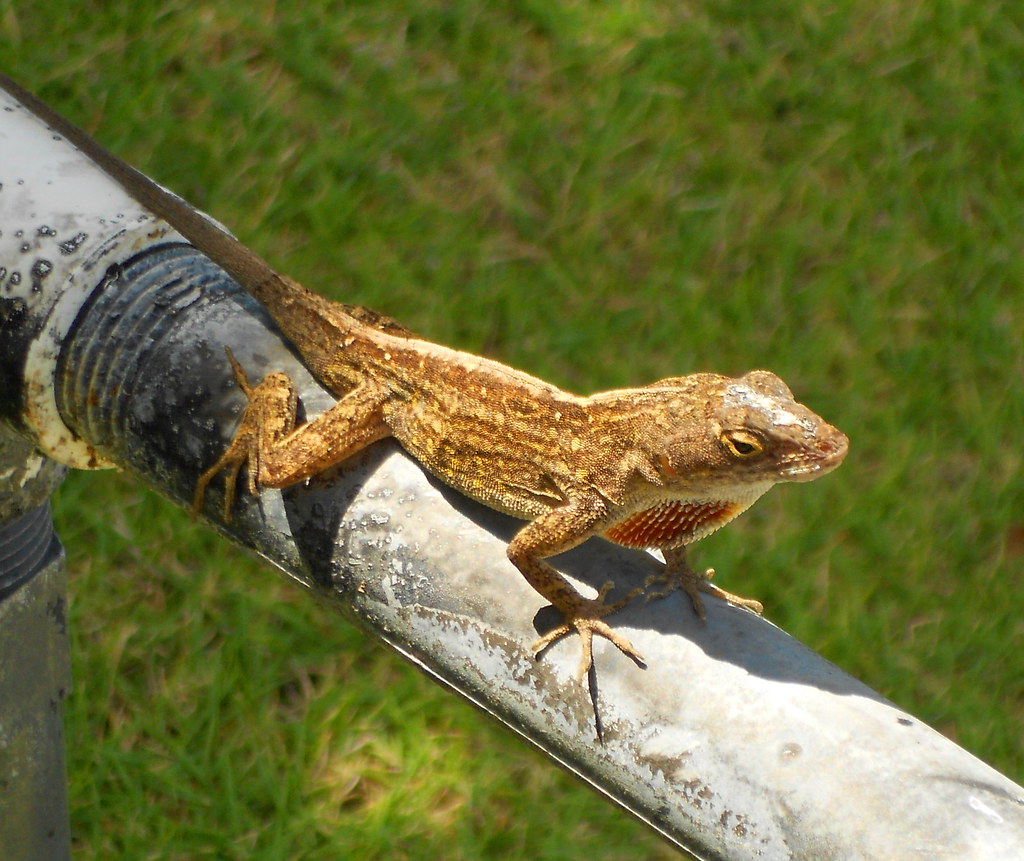
- Because lizards are mainly nocturnal, they have become a symbol for good vision and protection against the unseen things in life.
- Chinese lore says that pigs bring good luck to business dealings.
- In Korea, the swallow is considered a sign of good luck thanks to the story of Heungbu and Nolbu. According to the story, a sparrow rewarded a kind deed with prosperity.
- Egyptians looked at beetles, specifically the Egyptian scarab beetle, as lucky. These beetles wrap their eggs in mud and use the sun for incubation. Because of this ability to always find new life through the sun, Egyptians saw the scarab as a transmitter of luck.
Other Lucky Talismans
- Horseshoes are one of the oldest of lucky talismans, and there are varied legends associated with their strength. Suffice it to say that hanging a horseshoe on or above a door is still popular. Make sure that the points face up, making a U so that the horseshoe can fill with luck. Hanging the other way will allow all the luck to run out. Irish brides often carry a horseshoe instead of bouquet on their wedding day.
- “Lucky bamboo” is actually a close relative called Dracaena. It’s hardy and long-lived, which might account for its reputation as lucky. The more stalks a lucky bamboo plant has, the more luck it brings. A plant with three stalks is said to bring happiness, wealth, and longevity.
- During World War II, fighter pilots carried a variety of lucky charms with them in the hopes of tipping the odds in their favor and coming back alive. Gambling items like cards and dice were popular. Deccofelt Corp started marketing fuzzy dice to hang on the rearview mirrors of cars in 1959.
- A “Fumsups” (“thumbs-up”)is a tiny cherub-faced doll giving the lucky thumbs-up with both hands. They had metal bodies and wooden heads that allowed their owner to “touch wood” or “knock on wood” for good fortune. Fumsups were most popular during World War I, when they were given to soldiers. Some versions had a four-leaf clover painted on the doll’s head for an extra dose of good fortune.
- Hangman’s noose. The ropes were so valuable that hangmen were even known to cut them into pieces for sale as good luck charms. Sick people wrapped the ropes around their heads to cure headaches and fevers. This talisman was highly popular among gamblers and cardsharps. Other souvenirs of hangings were also considered lucky, but weren’t as reliably available.
- A caul is a piece of amniotic membrane that covers the face of newborn babies, albeit rarely. From ancient Rome till the 19th C, it was widely believed that having a piece of one would bring its owner good fortune, confer eloquence, good health and financial success. They were so prized that midwives were known to steal them.
- Bezoars are hardened, pearl-like clumps of indigestible matter that sometimes form in the stomach lining of animals. Around 1000 A.D., the stones became known as good luck charms throughout Europe and Asia. Bezoar stones were often mounted in elaborate gold settings or worn as protective amulets, but they were also prized for their supposed curative powers: an antidote to poisons and a cure for many other ailments including epilepsy, dysentery and the plague.
Doing Double Duty
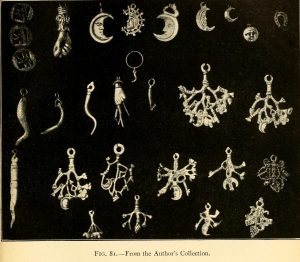
from Frederick Thomas Elworthy – The Evil Eye – page 203
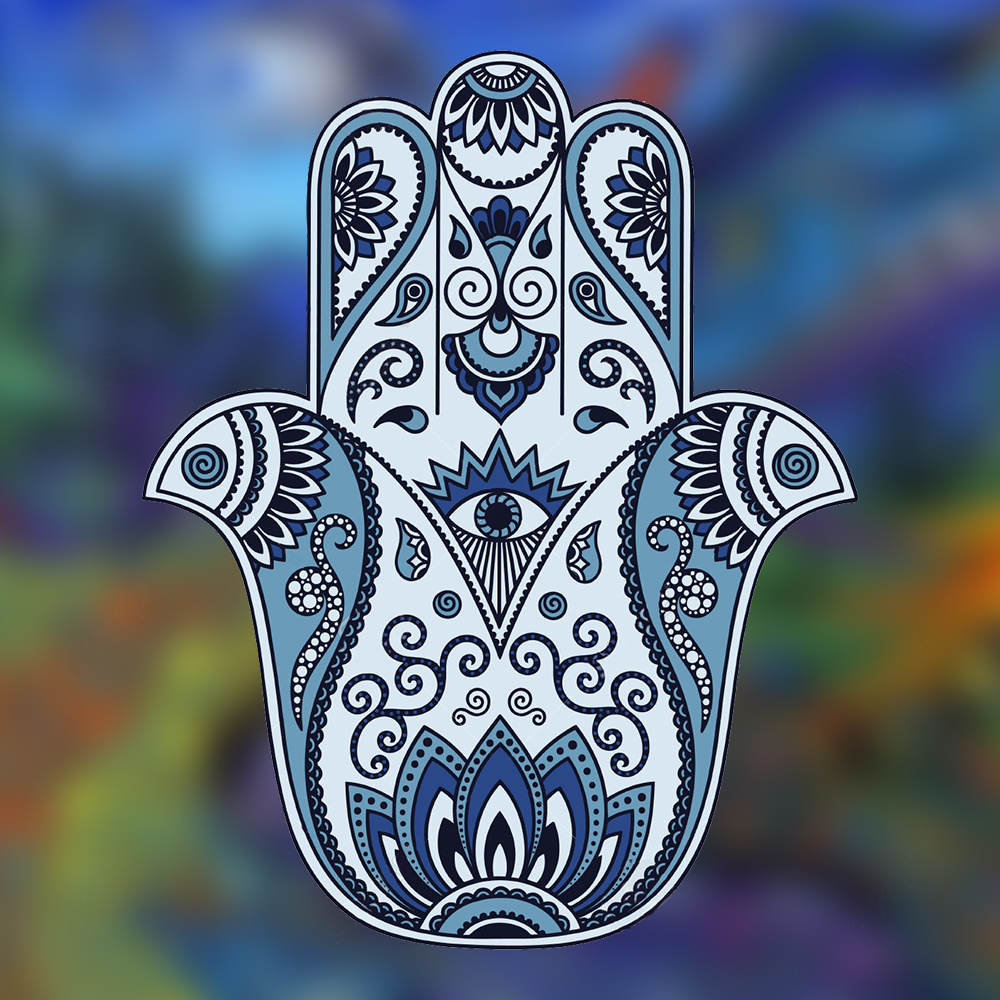
- Meaning “the Hand of God,” the Hamsa (from Hebrew חַמְסָה and Arabic خمسة) is a symbol many people in North Africa and Asia Minor have used to ward off the “evil eye” and dark spiritual forces. It is also thought to bring the wearer strength and blessings.
- Wearing a gem set in jewelry is used as a shield of protection to ward off troubles and bring happiness. Gems and minerals each are reputed to have specific beneficial properties, so consult a book of stones or search online for info about your favorite stones. (I’ve written more specifics about this before.)
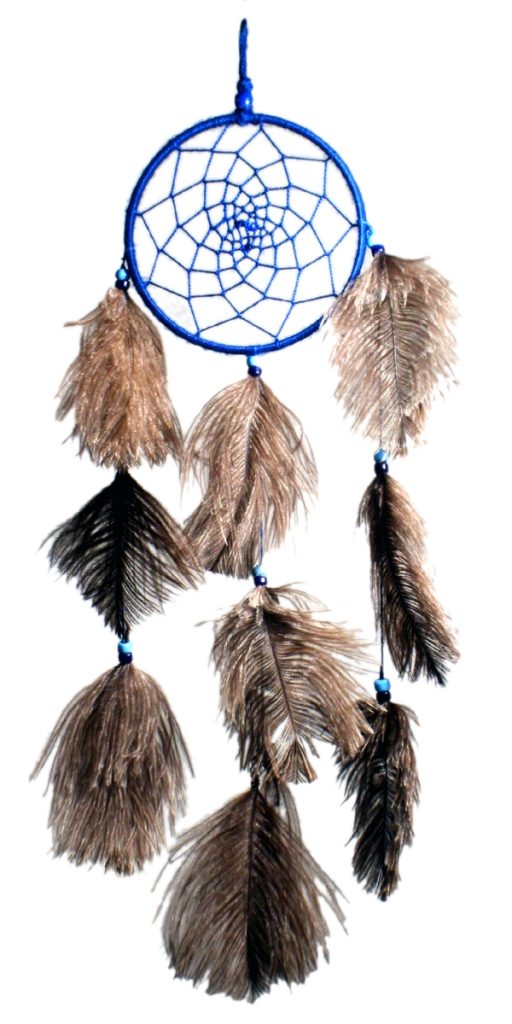
- Dreamcatchers are made with a web or net stretched over a loop and decorated with bright beads and feathers. They are said to catch bad dreams as they enter a household. By capturing disturbing dreams, they make the owner happier, more balanced, and luckier. Dreamcatchers can be used as wall art, earrings, etc.
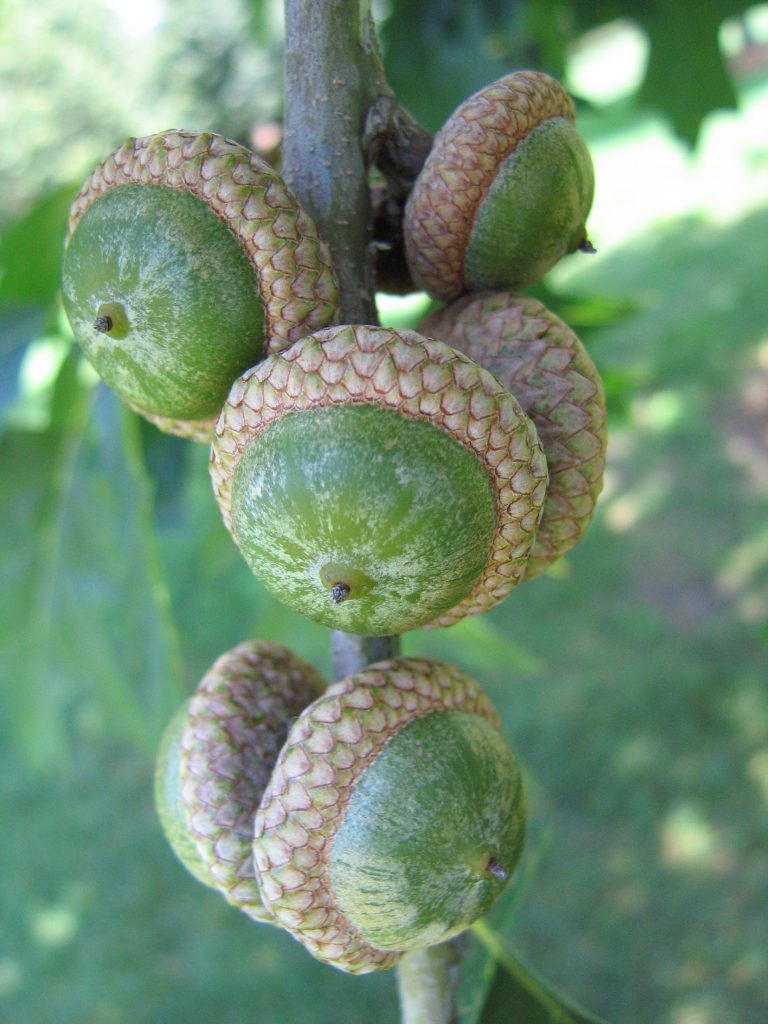
- Because of its association with the Norse god Odin, the acorn has come to symbolize wisdom. Acorns also signify fertility, youth, and prosperity. The Norse believed that acorns could bring divine protection and placed them in the windows of their homes to ward off lightning.




Portents of Things to Come
Bad
- Seeing a lizard scurrying away is a sign for you to flee trouble as well, before it occurs.
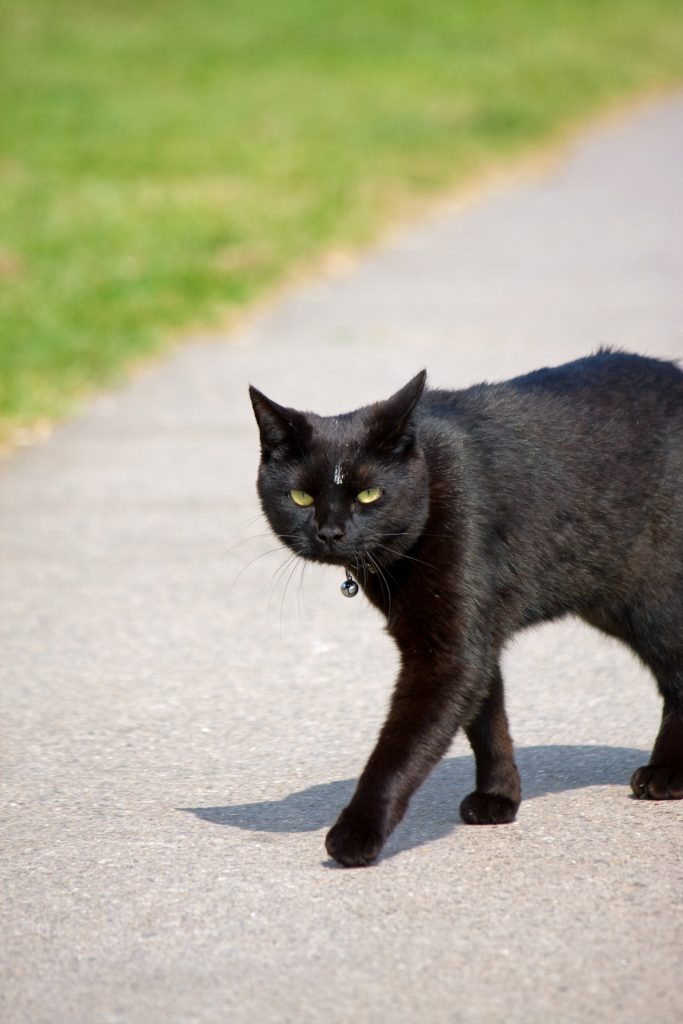
- Black cat crossing one’s path signals catastrophe to come.
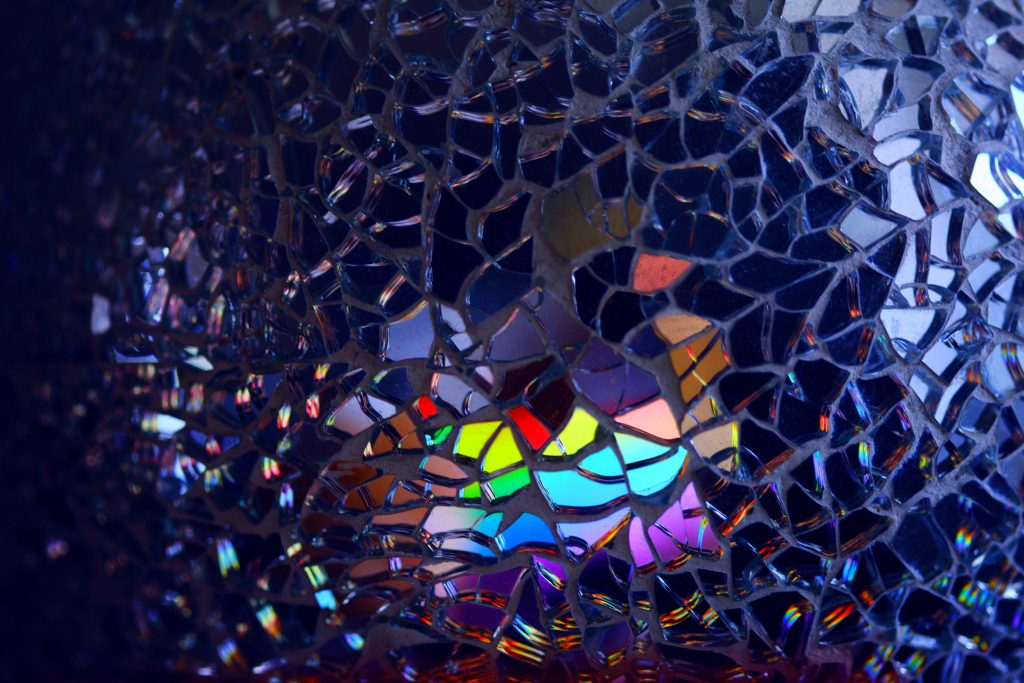
- Breaking a mirror causes seven years of bad luck.
- Walking under a ladder disrupts the Christian Holy Trinity, leading to divine retribution.
- Killing a ladybug hastens the killer’s death.




Good

- For the ancient Saxon people, spotting a rabbit was a sign of the spring to come.
- Seeing a rainbow, especially a double one, brings prosperity or peace, depending on the setting.
- Seeing an albatross portends good luck for sailors.
- According to legend, shaking a chimney sweep’s hand or passing one on the street is a harbinger of good fortune. The tradition is especially associated with weddings, so it’s particularly auspicious for couples to encounter chimney sweeps immediately after leaving the church. (Modern British chimney sweeps often supplement their income by hiring themselves out to wedding parties!)

We learn from Gay that the Lady-fly is used by the vulgar in E., in a similar manner for the purpose of divination.
“This lady-fly I take from the grass
Whose spotted back might scarlet red surpass?
Fly, lady-bird; north, south, or east or west
Fly where the man is found that I love best”.
from The Shepherd’s Week by John Gay, 1714
- Ladybugs are particularly fortuitous!
- If a man and a woman see a ladybug at the same time, they’ll fall in love.
- In Belgium, a ladybug crawling across a maiden’s hand meant that she would soon marry.
- A large number of ladybugs in the spring means there would be a good harvest.
- If a newlywed couple sees a ladybug, they can foretell how many children they’ll have by counting the ladybug’s spots.
- A ladybug inside your house signals a period of good fortune to come.
- Ladybugs on toys or clothes for infants bring health and good fortune.
- The Norse goddess Freya sent the ladybug to earth in a thunderbolt to bring good fortune and protection.
- The Hindu Indra Sanskrit Indra’s shepherd




Maybe
- Birds can symbolize many things to many people. Groups of nests, flight patterns, dropped feathers, spots on eggs, etc. mean all sorts of good or bad luck, depending on the setting. For more details, check out my previous blogs on Birds!
- Find a penny, pick it up, all the day you’ll have good luck—but only if it’s heads up. Tails up, find a penny, let it lay (or give it away) or bad luck you’ll have all day. Some people say that this is true; after all, any coin lying on the ground is luck.
Bottom Line: Talismans to bring luck and/or ward off bad luck are so varied, most people could accumulate dozens. Do they work? I could not say. They may be nothing more than a self-fulfilling prophecy, causing confidence boosts and selective confirmations. But as a scientist, I urge you to give them a try. If you do, and they make no difference, you’ve lost nothing. On the other hand, if they can make a difference and you ignore them, you’ve missed a chance big time.