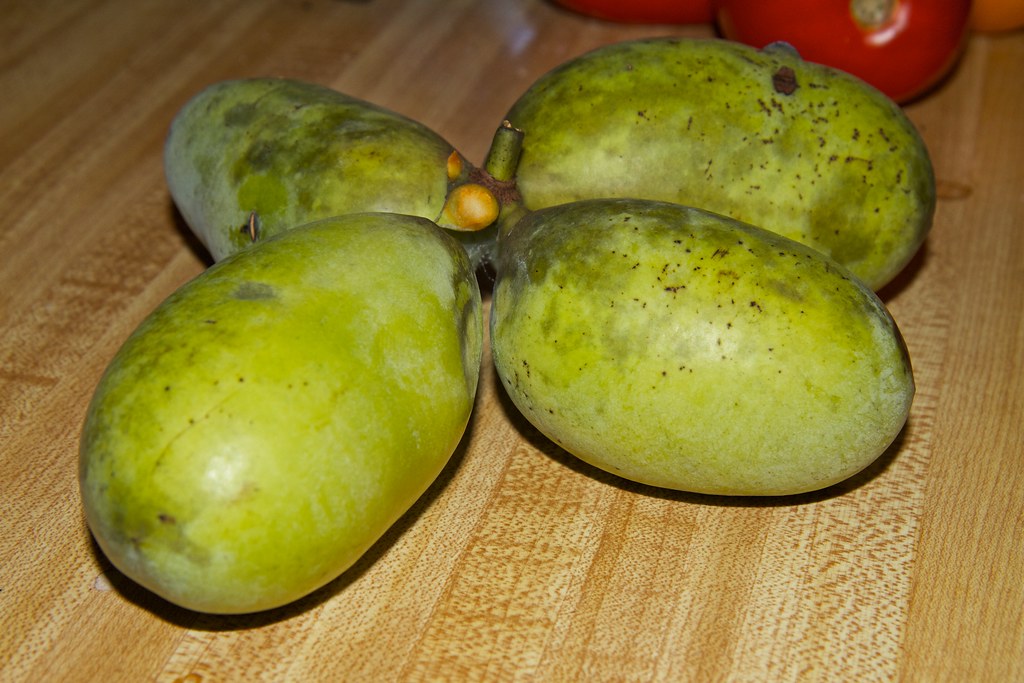
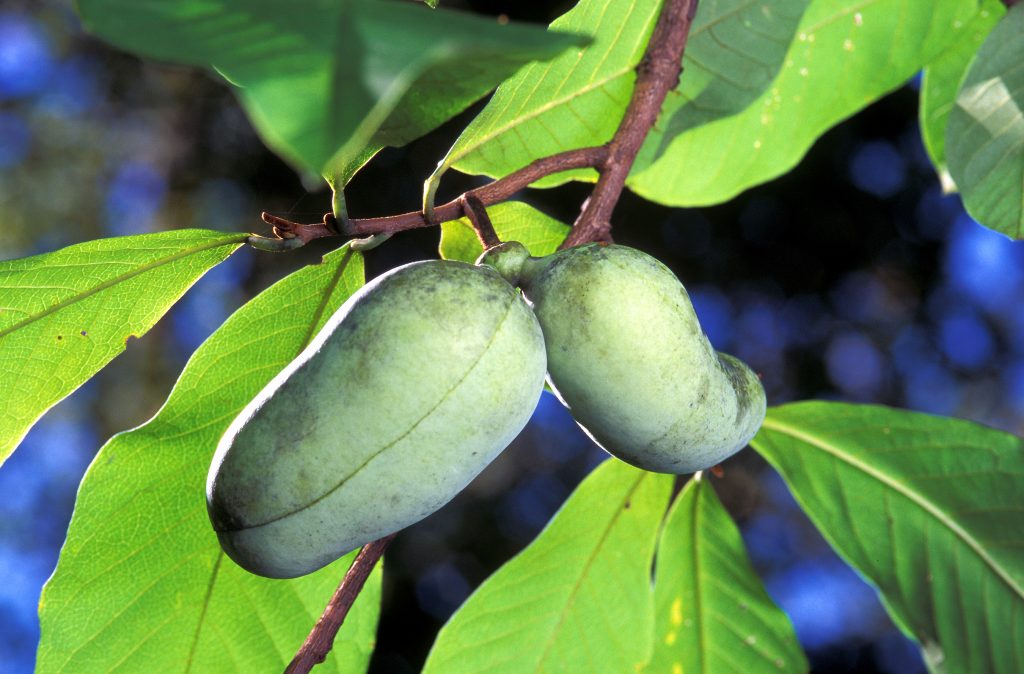
Periodically, a friend of a friend gifts me with a few pawpaws. Pawpaw (Asimina triloba) is a little known and (IMHO) not a pretty fruit. They are especially not pretty when left in the fridge during a week at the beach.
These are what remain of my most recent gift, received two days before I left town. Surprisingly, five of them are not just edible after a week in the fridge; they’re delicious. Which brings me to wax poetic—or at least, try to—about this fruit native to Virginia and most of the eastern United States and southern Canada.
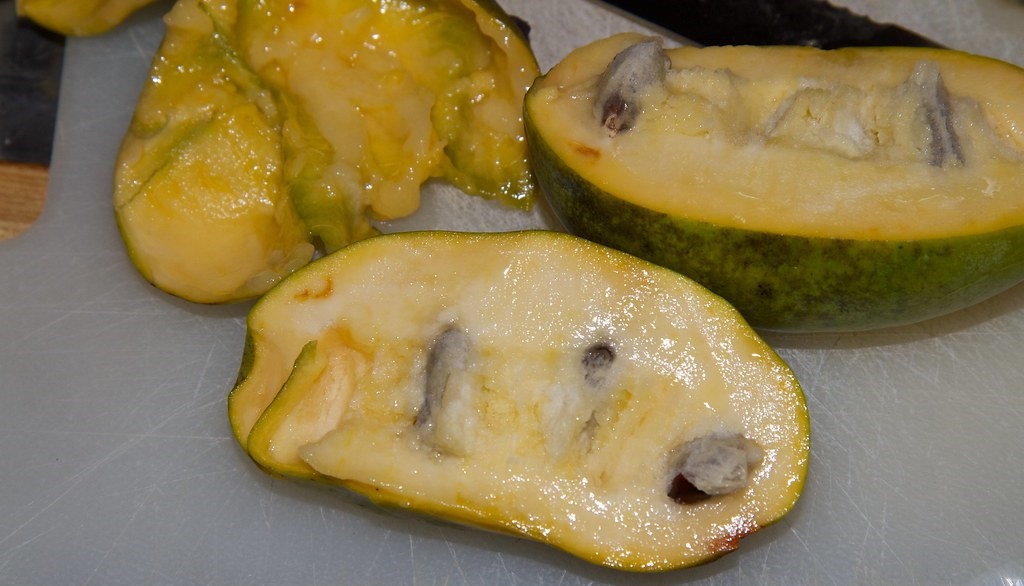
For one thing, it’s the only fruit native anywhere in North America that resembles tropical fruits. It is also the largest edible fruit native to North America. Open a pawpaw and you’ll find a sunshine-yellow pulp dotted with dark brown/black seeds. The flesh is the consistency of pudding and tastes like some combination of banana, mango, and pineapple. What’s not to love?
In 1541, a Portuguese explorer who accompanied explorer Hernando de Santo wrote, “The fruit is like unto Peares Riall [pears royal]; it has a very good smell and an excellent taste.”
Pawpaws are high in vitamin C, magnesium, iron, copper, and manganese. They are a good source of potassium and several essential amino acids, and they also contain significant amounts of riboflavin, niacin, calcium, phosphorus, and zinc.
I eat it “as is” but people who have enough to save for later can freeze the flesh for baking, or make it into preserves. Pawpaws will not ripen if plucked from the tree too early, but unripe pawpaws can ferment into a sweet wine that pawpaw connoisseurs highly prize.
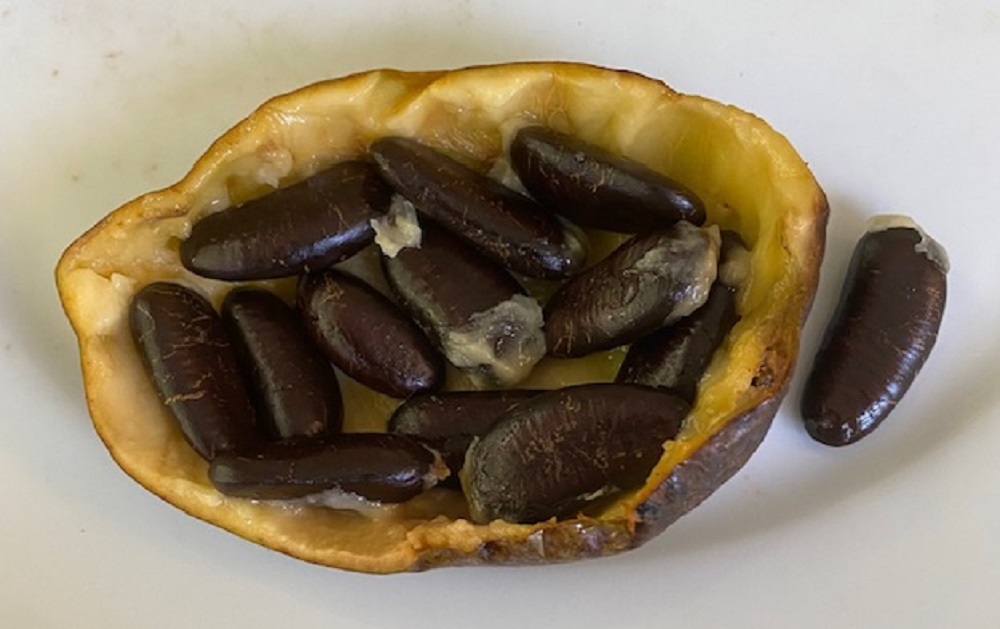
And about those seeds: as the largest edible fruit native to North America (5-16 oz., 3-6 inches long), there is plenty of room for seeds. The seeds are reminiscent of lima beans in shape, and adorn the flesh in two rows, 10-14 seeds per fruit. Each seed is 1/2 to 1-1/2 inches. Reputedly, pawpaws grow easily from seeds, but I’ve never tried. In the wild, pawpaws send out suckers, creating the “pawpaw patch” of song. Pawpaw cultivators frequently grow new trees from grafts and can produce fruit up to a pound and a half in size.
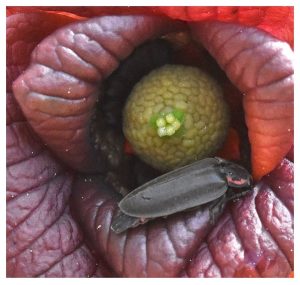
When sucked clean, the seeds feel satin smooth. One might be tempted to carry one as a lucky charm or worry “stone.” I can imagine these seeds used in children’s games: money, tokens… But if one chooses to play with dry pawpaw seeds, be aware that dry seeds won’t germinate.
Unlike most fruit trees, pawpaws do not attract bees for pollination. The flowers attract carrion flies and beetles. Pawpaw leaves are the only host for zebra swallowtail butterfly larva.
Pawpaw History
If you aren’t familiar with pawpaws, you aren’t alone. You might know them as a poor man’s banana, Indiana banana, prairie banana, frost banana, custard apple, fetid-bush, or bandango. They aren’t easy to store or ship and so haven’t been developed as a commercial food until recently. Food scientist Neal Peterson is one of many pawpaw enthusiasts who has spent decades breeding and cultivating pawpaws to make them commercially viable, greatly widening their availability.
But they were a key component of American Indian diets; indeed, the Shawnee even had a “pawpaw month” (ha’siminikiisfwa) when they harvested and preserved pawpaws. It was a cultivated food for many tribes along the Eastern Seaboard. Archaeologists have found huge quantities of pawpaw seeds and remnants at the sites of the earliest Native American settlements all along the east coast of North America.
A wise move, because pawpaws are incredibly nutritious.
At least two U.S. presidents favored pawpaws: reportedly, they were George Washington’s favorite dessert. Thomas Jefferson grew pawpaws at Monticello and had the seeds shipped to friends in Paris when he was the American ambassador to France.
Journal entries document that pawpaws fed the Lewis & Clark expedition on their return trip in the fall of 1810. In fact, pawpaw fruits and nuts saved the expedition from starvation and death when in western Missouri their rations ran low and no game was to be found.
Our party entirely out of provisions. Subsisting on poppaws. We divide the buiskit [sic] (biscuits) which amount to nearly one buisket [sic] per man, this in addition to the poppaws is to last us down to the Settlement’s which is 150 miles.
William Clark (Lewis & CLark Expedition)
For a time, many European settlers viewed the pawpaw as a marker of racial difference, according to food historian Rebecca Earle. As ideas about racial and societal divides developed and codified, white settlers often dismissed pawpaws. Rejecting “different” foods, including pawpaws, as fit only for “different” races, became part of the colonial identity.
Their hardiness and tendency to grow wild made pawpaws a common food source along several areas of the Underground Railroad.
During the Great Depression, people often ate pawpaws as a substitute for other fruits, hence their nickname “poor man’s bananas.” Though the pawpaw continued to be an important fruit in the North American diet, interest waned after World War II with the introduction of other fruits. Racist views of the pawpaw’s place in the American diet contributed to its marginalization. As Dr. Devon Mihesuah, a scholar of Indigenous foodways, says, pawpaws haven’t been forgotten so much as “ignored, disliked, and unavailable.”

Joe Grant Pawpaw
by Cbarlow
Nowadays, most pawpaws are very difficult to find outside of a few local farm markets, though some breeders are working to change that. The Cattawba Nation has started a food sovereignty program, including planting a pawpaw orchard. Every year, the Ohio Pawpaw Festival celebrates all the possibilities of this uniquely American fruit.
Although not a place name in Virginia, many states have named towns and villages after pawpaws, including Paw Paw, WV; Paw Paw, KY; Paw Paw, OK; and numerous others towns in Illinois, Ohio, and Indiana. In Michigan, the Paw Paw River drains into the Paw Paw Lake and Little Pawpaw Lake, skirting by the town of Paw Paw. Natchitoches, LA, translates to “pawpaw eaters,” a name given by the Caddo.
Folklore
In the fall, Buck Run bananas [pawpaws] are ripe – in the frost fall, a wise man takes a wife.
Tennessee wisdom
Rural populations relied heavily on pawpaw fruit as a food source, so naturally other parts of the tree figured heavily in medicine and folklore traditions. In some communities, people wore pawpaw seeds as an amulet to prevent disease. Shawnee and Catawba artisans used pawpaw bark fiber to make fishing nets and lines, weaving designs for luck and good fish catches into the nets.
Pawpaws offered powerful protection against Ozark Witches. Ozarkers used many means to thwart witches, especially to protect the home. One method was driving several tiny pegs of pawpaw wood into the doorsill.
The (supposedly) powerful Pawpaw Conjure used wood from the pawpaw tree:
This charm could be employed if the witch master could obtain the witch’s nail parings, a lock of hair, a tooth, or a cloth with her blood on it. The hair, nail parings, or other personal effects were stuck to the end of a wooden peg with beeswax. The witch master took this peg out into the woods at midnight, bored a hole in the fork of a pawpaw tree, and drove the peg into the hole. The witch, and her powers, were expected to dwindle.
owennativefoods.com
BOTTOM LINE: Get thee to the pawpaw patch. I recently learned that Richmond has a pawpaw walk along the river, free for the taking!