I’m sure there are many people out there who know a lot more about superheroes than I do. Before researching this blog, I would have been pressed to name any beyond Wonder Woman, possibly coming up with Bat Girl and Sheena, Queen of the Jungle. Like so many things on the internet, seek and ye shall find!
The Golden Age of creating these female superheroes seems to have been 1940-1941. Subsequently, many of them made it to both the small screen and the big one, and—like James Bond—appeared and reappeared. (See those marked with *.)
Here, in chronological order, are a few of the very first female superheroes who might interest you as a reader and/or a writer. This is Part 1 of 2, covering female comic stars who debuted through 1940. Heroic ladies who debuted in 1941 and after will be covered on Tuesday, March 23rd.
If your character has a superhero interest, who and why? What superpowers might they wish for? How about a secret superhero crush?
1938
- Sheena, Queen of the Jungle
- Sheena debuted almost four years before Wonder Woman. She was the guardian of the jungle, with numerous superpowers: superhuman strength, the ability to talk to animals, and expertise with several weapons, mostly blades. Sheena was one of the most powerful superheroes.
1940
- Fantomah
- The “Mystery Lady of the Jungles” was the protector of the entire continent of Africa. Fantomah was a supernatural being with superhuman abilities, including telekinesis and the ability to turn into a blue-skinned monster. Her origins were never revealed, nor was the reason she had fair skin and had blond hair.
- Initially, Fantomah was almost identical to Sheena. As she developed, Fantomah became nearly omnipotent, creating some truly bizarre punishments for slavers, poachers, thieves, and others she decided to punish. At one point, she became the queen of a lost civilization descended from the Egyptians. The writers got tired of that storyline, and the civilization became lost again.
- *Hawkgirl/ Hawkwoman
- Depending on the comic run, Hawkgirl is either the reincarnation of an Ancient Egyptian princess or an alien police officer from planet Thanagar. Or she is both at the same time but in parallel universes. Or maybe she is the reincarnated spirit of an Ancient Egyptian priestess who is actually the avatar of a goddess who is now inhabiting the body of a winged alien police officer. The writers kept changing their minds.
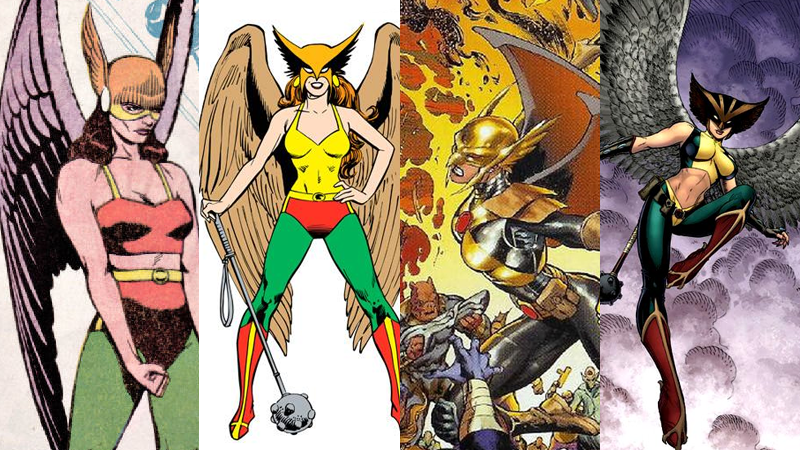

- However she came by her powers, Hawkgirl has superhuman strength, speed, durability, and advanced healing. Her wings are incredibly strong for their size and let her perform extreme acrobatic flight maneuvers.
- *Catwoman
- In her first appearance in Batman #1, Selina Kyle was simply known as The Cat. Originally, she was either an orphan who learned thievery to survive on the streets or a former flight attendant with amnesia who turned to crime with no memory of any former skills. An enduring love interest of Batman, Catwoman was recently (partially) reformed from her more criminal activities. She’s an expert cat burglar with acrobatic prowess. She prefers to rely on her brains and a whip. She prowls the streets helping those who need her most, but she also steals from the evil rich to help those in need and fill her own coffers.
- *Catwoman was reintroduced in 1989, but this time she was portrayed as either a prostitute or a dominatrix who was inspired to become a costumed cat burglar after watching Batman’s antics.
- Lady Luck
- Brenda Banks was the very rich daughter of wealthy Irish mine owners who simply got bored and decided to put on a disguise and fight evil. She was aided by her chauffeur (sometimes a burly Italian man and sometimes a woman trained in martial arts). Lady Luck has no superpowers (other than being Irish), but she was a terrific fighter. The storyline revolved around her being in love with the Chief of Police.
- Golden Girl
- Making her first appearance in the world of Captain America, Elizabeth “Betsy (originally Betty)” Ross became a costumed hero in her own right after impressing Allied intelligence forces. She started out as a WAAC officer and FBI agent before she became part of the SSR project to create supersoldiers. After World War II, Ross put on a bulletproof cape and joined the third Captain America as Golden Girl. Because of her various careers (soldier, spy, teacher, dancer, etc.), Golden Girl had many talents, but no superpowered abilities. Her intelligence kept her in the ranks of superheroes.
- This Betty/ Betsy Ross is not related to Betty Ross, the romantic interest of Bruce Banner/ The Incredible Hulk.
- Red Tornado
- Abigail Mathilda “Ma” Hunkel was initially intended to be a parody of the superhero comic genre, but the Red Tornado grew so popular that she became a regular co-star in the Scribbly Jibbet comics. A shopkeeper and housewife in Brooklyn, Ma Hunkel stood up to a gang harassing her neighborhood by taking inspiration from her son’s obsession with the Green Lantern. She became a caped vigilante by wearing a t-shirt over red long-johns, a black cape, and a cooking pot with eye holes. The Red Tornado was extremely strong and durable but not superhuman (she was sometimes mistaken for a man). She eventually had two sidekicks, her daughter and niece, Sisty and Dinky. Additionally, Ma Hunkel was a fantastic cook and honorary member of the Justice League.

- *Black Widow
- Claire Voyant, created in August, 1940, by Timely Comics (later known as Marvel Comics), might be the first female superhero to be possessed by a mystical being. She and her family were murdered, and she made a deal with the devil in order to return to seek revenge. Her superpowers: she could use psychic powers, defy physics, curse enemies with severe bad luck, and kill people instantly with a touch. Black Widow was resistant to disease and aging, and could suppress and/or replace memories.
- During World War II, she helped the Allies by spying and by killing Nazis to send their souls to Satan. In the Battle of Berlin, Black Widow was captured by Nazi scientists and put in suspended animation with several other superheroes. The Twelve were found and woken up in the 21st Century to continue working for the US government.
- She is not related to the Black Widows created by the Soviet Red Room program.

- The Woman in Red
- She first appeared in March 1940 in Thrilling Comics. Along with Lady Luck she was one of the first vigilante female superheroes. Peggy Allen donned red after getting fed up with criminals manipulating the legal system and avoiding justice. Her real job was as a police officer specializing in undercover work, so one might label her a rogue cop. The Woman in Red had no special superpowers, but was highly skilled in hand-to-hand combatant and a brilliant tactician.
- There were essentially three versions of the Woman in Red, depending on the writer.
- Initially, Peggy Allen was taller and stronger than most men, knew a bit of jiu-jitsu but quite a lot about shooting her pistol, and was not trusted by the police.
- In the middle of 1941, Peggy Allen became a woman of average size and strength, a very good detective, and an ally of the police.
- The Peggy Allen of 1943 had near superhuman strength and agility, was a skilled martial artist and pilot, and worked with the police, who knew her secret identity. In 1943, the Woman in Red also got a costume change before disappearing.
- There were essentially three versions of the Woman in Red, depending on the writer.
Bottom Line: Long as the list is, these female superheroes are just the beginning! Check back on the 23rd for more pioneering superheroes. There is much more information online. For example, the wrap.com/female-superheroes-badass-memorable-batwoman-supergirl/. Also, gamesradar.com/best-female-superheroes/. And car.com/female-superheroes-created-before-wonder-woman/