Papua New Guinea was long isolated from the rest of the world. The island is mountainous, and tribes located in tiny villages have warred with one another for five hundred generations. Even today, almost a thousand languages can be found (approximately 12% of all the languages spoken in the world). It is a wild place, where the outside world has had little influence, and cannibalism may be practiced, though there is some debate on how widespread the custom is today.
Actually, the only tribe which may still practice cannibalism is the Korowai tribe (a.k.a. Kolufu) in south-eastern Papua/south-eastern part of the western part of the New Guinea. But still, that is one marker of how very different human societies can be.
Archeological records suggest that pigs were introduced to New Guinea between 2,500 and 10,000 years ago, by way of a land bridge to Asia that has since disappeared. Pigs play important roles among the peoples of Papua, especially so among those living in the Central Highlands.
Apart from pigs and deer (originally brought in by the Europeans) there are not many mammals on these islands. So, yes, pigs are bred for their meat, but they are rarely killed just for eating.
The Pig Culture
In a section known as Kaulong, a pig culture prevails. The people believe pigs and humans are on a single continuum of existence, such that pigs may behave more or less like humans and humans may behave more or less like pigs.
Villagers say, “Pigs are our hearts!” Young pigs are treated as pets: they share their owner’s cooked food, are ritually named and baptized, are given magical treatments for illness, and women pre-chew tubers to feed to weak piglets.
The men own the pigs. Although there is some assertion that women or children (rarely) own a pig, the counter argument is that the man has “given the pig into their care” and thus they speak of it as their own.
Raising pigs is an important responsibility, and there is no argument that women are the ones who care for these precious animals.
At birth, powdered lime is blown into the nostrils of the piglet to make it forget its natural mother and cause it to bond with its human one.
Pigs are named, and share the women’s sleeping quarters. The women pet and handle them. Occasionally, small pigs unable to compete against siblings or orphaned piglets were breast fed by nursing mothers.
(If you search for “woman suckling pig” online, you can find images: a Huli woman breast feeding a child and a piglet the same time; and a Chimbu woman in the Eastern Highlands of Papua New Guinea breast feeding a piglet.)
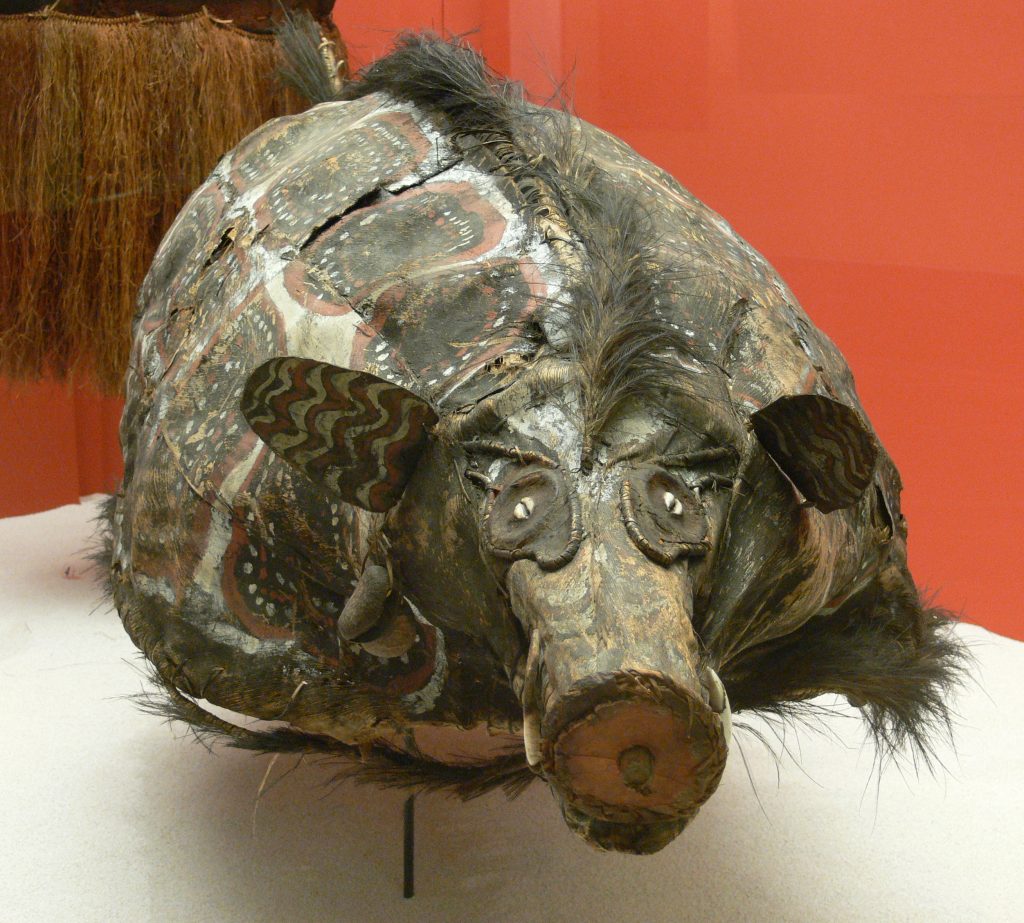

Pigs as Part of Ceremonies
Pigs are sacrificed in some places to appease the ancestral spirits, and they play central roles at major rites of passage: births, weaning of children, initiation of boys, a girl’s first menstruation, weddings, and funerals. The most frequent occasion for eating pig meat is a funerary cremation.
Pig killing/eating accompanies many undertakings, such as house building and boat building.

Much feasting accompanies festivals in which local men of influence match themselves in prestige competitions.
Pigs are exchanged at peacemaking ceremonies after violent disputes.
A special occasion at which pig meat is eaten every day for weeks on end by men, women, and children, is during the major pig feasts, held at regular intervals.
There are two exceptions: a pig which is sick, and a pig which has been stolen. Such pigs would be consumed as soon as possible, without the usual ceremony.
Pigs for Status and Trade
Pigs are important symbol of political and social power. The more pigs an individual has, the more pigs he can give away, leading to bigger feasts and a higher social status.
Pigs are the main dowry offered in exchange for brides.
The most valuable pig to own is a “tusker.” These are pigs which have had their upper canines removed by a specialist, so that their lower canines can grow unimpeded, sometimes—after ten or twelve years—turning in a full circle to re-enter the lower jaw. After the ceremonial removal, the owner will use spells and all-night ceremonies to enhance that growth.
Adult tribe members blacken their own teeth with manganese oxide because white, visible teeth signify aggression (like a pig’s tusks). Tusks are made into ornaments, which a man must kill another man to earn permission to wear. When men are challenging another tribe in battle, they clench pigs’ tusks between their own teeth to appear more aggressive: “Watch out. I can be like a pig. I am powerful and dangerous.”
BOTTOM LINE: Pigs are a very valuable commodity in this part of the world, because they are used to buy brides, in general commerce and trading, for feasts and important ceremonies. Pig ownership is a sign of a man’s wealth. Thus—at (virtually) all costs—pigs are kept alive and pampered until needed. Seems like hog heaven to me!